Building MLflow evaluation datasets
To systematically test and improve a GenAI application, you use an evaluation dataset. An evaluation dataset is a selected set of example inputs — either labeled (with known expected outputs, i.e. ground-truth expectations) or unlabeled (without ground-truth). Evaluation datasets help you improve your app's performance in the following ways:
- Improve quality by testing fixes against known problematic examples from production.
- Prevent regressions. Create a "golden set" of examples that must always work correctly.
- Compare app versions. Test different prompts, models, or app logic against the same data.
- Target specific features or isolate certain problems in your agent. Build specialized datasets for safety, domain knowledge, or edge cases.
- Validate the app across different environments (e.g., development vs. production) as part of LLMOps.
You can think of them as test suites or benchmarks for your LLM functionality.
Requirements
Evaluation Datasets require an MLflow Tracking Server with a SQL backend (PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite, or MSSQL). This feature is not available in FileStore (local file system-based tracking). If you need a simple local configuration for MLflow, use the sqlite option when starting MLflow.
- An evaluation dataset is attached to an MLflow experiment. If you do not already have an experiment, see Create an MLflow Experiment to create one.
Data sources for evaluation datasets
You can use any of the following to create an evaluation dataset:
- Existing traces. If you have already captured traces from a GenAI application, you can use them to create an evaluation dataset based on real-world scenarios.
- Manually created examples. Define test cases by hand using dictionaries or DataFrames. This is useful for targeting specific edge cases or creating "golden" test cases that must always pass.
This page describes how to create an MLflow evaluation dataset. You can create datasets from traces using either the MLflow Monitoring UI or the SDK. You can also use other types of datasets, such as Pandas DataFrames or a list of dictionaries. See Evaluation examples for more examples.
Create or update a dataset using the UI
Follow these steps to use the UI to create a dataset or add to a dataset from existing traces.
-
Click Experiments in the sidebar to display the Experiments page.
-
In the table, click on the name of your experiment to open it.
-
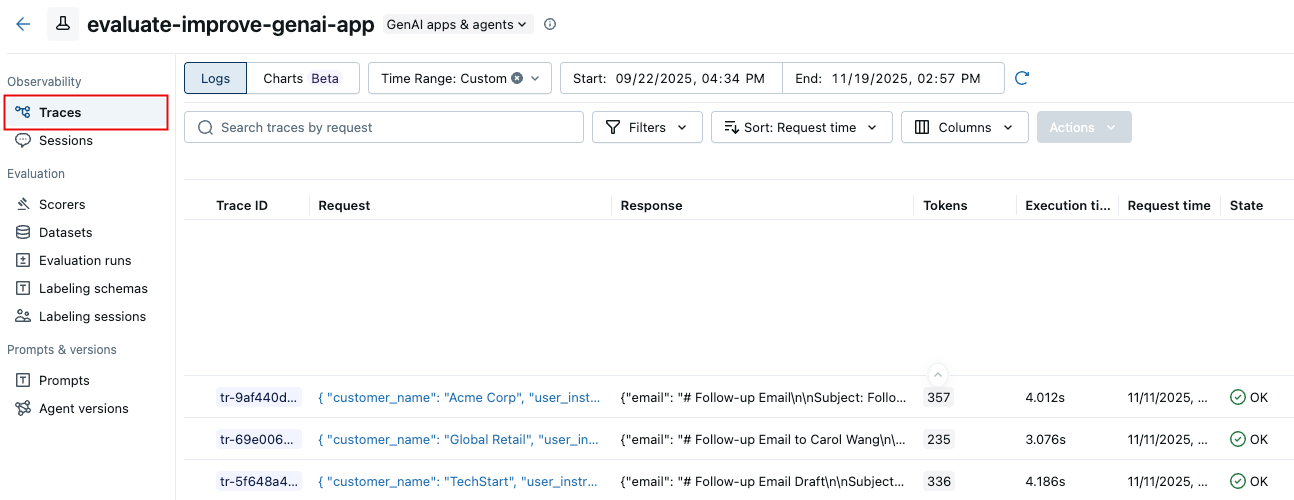
In the left sidebar, click Traces.
-
Use the checkboxes to the left of the trace list to select traces to export to your dataset. To select all traces, click the box next to Trace ID.
-
Click Actions. From the drop-down menu, select Add to evaluation dataset.
-
The Export traces to evaluation dataset dialog appears.
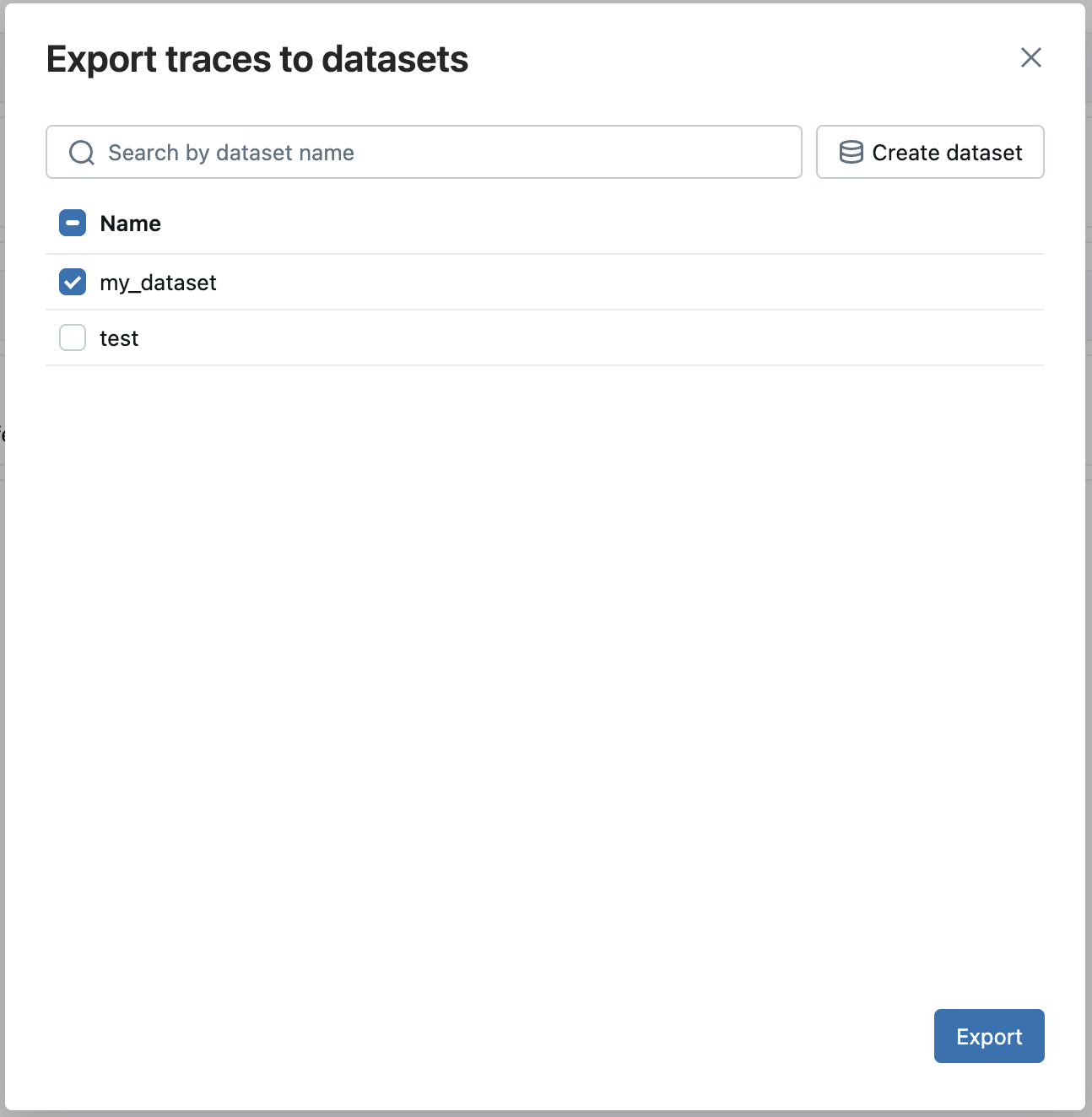
If evaluation datasets exist for this experiment, they appear in the dialog.
- Click Export next to the dataset you want to add these traces to.
If no evaluation dataset exists for the experiment:
- Click Create new dataset.
- In the Create Dataset dialog, enter a name for the evaluation dataset and click Create.
- Click Export next to the dataset you just created.
Create a dataset using the SDK and add records
This section describes several options for adding records to the evaluation dataset.
- From existing traces
- From Dictionaries
- From DataFrame
One of the most effective ways to build a relevant evaluation dataset is by curating examples directly from your application's historical interactions captured by MLflow Tracing.
Programmatically search for traces and then add them to the dataset using search_traces(). Use filters to identify traces by success, failure, use in production, or other properties. See Search traces. You can also add ground-truth expectations to your traces before or after adding them to an evaluation dataset using log_expectation().
import mlflow
from mlflow.genai.datasets import create_dataset, set_dataset_tags
# Create your evaluation dataset
dataset = create_dataset(
name="production_validation_set",
experiment_id=["0"], # "0" is the default experiment
tags={"team": "ml-platform", "stage": "validation"},
)
# Optionally, add additional tags to your dataset.
# Tags can be used to search for datasets with search_datasets API
set_dataset_tags(
dataset_id=dataset.dataset_id,
tags={"environment": "dev", "validation_version": "1.3"},
)
# 2. Search for traces
traces = mlflow.search_traces(
filter_string="attributes.name = 'chat_completion' AND tags.environment = 'production'",
order_by=["attributes.timestamp_ms DESC"],
max_results=10,
)
print(f"Found {len(traces)} successful traces")
# 3. Add expectations to the traces
for trace in traces:
mlflow.log_expectation(
trace_id=trace.info.trace_id,
name="expected_answer",
value=("Correct answer for this input"),
)
# 4. Add the traces to the evaluation dataset
eval_dataset = eval_dataset.merge_records(traces)
print(f"Added {len(traces)} records to evaluation dataset")
Select traces for evaluation datasets
Before adding traces to your dataset, identify which traces represent important test cases for your evaluation needs. You can use both quantitative and qualitative analysis to select representative traces.
Quantitative trace selection
Use the MLflow UI or SDK to filter and analyze traces based on measurable characteristics:
- In the MLflow UI: Filter by tags (e.g.,
tag.quality_score < 0.7), search for specific inputs/outputs, sort by latency or token usage - Programmatically: Query traces to perform advanced analysis
import mlflow
import pandas as pd
# Search for traces with potential quality issues
traces_df = mlflow.search_traces(
filter_string="tag.quality_score < 0.7",
max_results=100,
extract_fields=[
"span.end_time",
"span.inputs.messages",
"span.outputs.choices",
"span.attributes.usage.total_tokens",
],
)
# Analyze patterns
# For example, check if quality issues correlate with token usage
correlation = traces_df["span.attributes.usage.total_tokens"].corr(
traces_df["tag.quality_score"]
)
print(f"Correlation between token usage and quality: {correlation}")
For complete trace query syntax and examples, see Search Query Syntax.
Qualitative trace selection
Review individual traces to identify patterns requiring human judgment:
- Examine inputs that led to low-quality outputs
- Look for patterns in how your application handled edge cases
- Identify missing context or faulty reasoning
- Compare high-quality vs. low-quality traces to understand differentiating factors
Once you've identified representative traces, add them to your dataset using the search and merge methods described above.
You can also use AI Insights features like Analyze Experiment to automatically discover quality and operational issues across your traces.
You can curate examples from scratch. Your data must match (or be transformed to match) the evaluation dataset schema.
import mlflow
from mlflow.genai.datasets import create_dataset
# Create dataset with manual test cases
dataset = create_dataset(
name="regression_test_suite",
experiment_id=["0", "1"], # Multiple experiments
tags={"type": "regression", "priority": "critical"},
)
# Define test cases with expected outputs (ground truth)
test_cases = [
{
"inputs": {
"question": "How do I reset my password?",
"context": "user_support",
},
"expectations": {
"expected_answer": (
"To reset your password, click 'Forgot Password' on the login page, "
"enter your email, and follow the link sent to your inbox"
),
"must_contain_steps": True,
"expected_tone": "helpful",
},
},
{
"inputs": {
"question": "What are your refund policies?",
"context": "customer_service",
},
"expectations": {
"expected_answer": (
"We offer full refunds within 30 days of purchase. "
"Refunds after 30 days are subject to approval."
),
"must_include_timeframe": True,
"must_mention_exceptions": True,
},
},
]
dataset.merge_records(test_cases)
import pandas as pd
from mlflow.genai.datasets import create_dataset
# Create dataset
dataset = create_dataset(
name="benchmark_dataset",
experiment_id=["0"],
tags={"source": "benchmark", "version": "2024.1"},
)
# Create DataFrame with inputs and expectations (ground truth)
df = pd.DataFrame(
[
{
"inputs": {
"question": "What is MLflow?",
"domain": "general",
},
"expectations": {
"expected_answer": "MLflow is an open-source platform for ML",
"must_mention": ["tracking", "experiments", "models"],
},
},
{
"inputs": {
"question": "How do I track experiments?",
"domain": "technical",
},
"expectations": {
"expected_answer": "Use mlflow.start_run() and mlflow.log_params()",
"must_mention": ["log_params", "log_metrics"],
},
},
{
"inputs": {
"question": "Explain model versioning",
"domain": "technical",
},
"expectations": {
"expected_answer": "Model Registry provides versioning",
"must_mention": ["Model Registry", "versions"],
},
},
]
)
# Add records from DataFrame
dataset.merge_records(df)
Preview the dataset
Optionally, you can examine the dataset by converting it to a dataframe.
df = eval_dataset.to_df()
print(f"\nDataset preview:")
print(f"Total records: {len(df)}")
print("\nSample record:")
sample = df.iloc[0]
print(f"Inputs: {sample['inputs']}")
Understanding Source Types
Every record in an evaluation dataset has a source type that tracks its provenance. This enables you to analyze model performance by data origin and understand which types of test data are most valuable.
Update existing datasets
You can use the UI or the SDK to update an evaluation dataset. For UI instructions, see Create or update a dataset using the UI.
To use the MLflow SDK to update and existing evaluation dataset:
import mlflow.genai.datasets
import pandas as pd
# Load existing dataset
dataset = mlflow.genai.datasets.get_dataset(name="eval_dataset")
# Add new test cases
new_cases = [
{
"inputs": {"question": "What are MLflow models?"},
"expectations": {
"expected_facts": ["model packaging", "deployment", "registry"],
"min_response_length": 100,
},
}
]
# Merge new cases
dataset = dataset.merge_records(new_cases)
Next Steps
Ready to improve your GenAI testing? Start with these resources:
Dataset Structure
Understand how evaluation datasets organize test inputs, expectations, and metadata
Setting Expectations
Learn how to define ground truth and expected outputs for your AI system
Evaluation Framework
Run systematic evaluations using your datasets with automated scorers