Create a custom judge using make_judge()
Custom judges are LLM-based judges that evaluate your GenAI agents against specific quality criteria. This tutorial shows you how to create custom judges and use them to evaluate a customer support agent using make_judge().
You will:
- Create a sample agent to evaluate
- Define three custom judges to evaluate different criteria
- Build an evaluation dataset with test cases
- Run evaluations and compare results across different agent configurations
Step 1: Create an agent to evaluate
Create a GenAI agent that responds to customer support questions. The agent has a (fake) knob that controls the system prompt so you can easily compare the judge's outputs between "good" and "bad" conversations.
- Initialize an OpenAI client to connect to OpenAI-hosted LLMs. Use the native OpenAI SDK to connect to OpenAI-hosted models. Select a model from the available OpenAI models.
import mlflow
import os
import openai
# Ensure your OPENAI_API_KEY is set in your environment
# os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "<YOUR_API_KEY>" # Uncomment and set if not globally configured
# Enable auto-tracing for OpenAI
mlflow.openai.autolog()
# Create an OpenAI client connected to OpenAI SDKs
client = openai.OpenAI()
# Select an LLM
model_name = "gpt-4o-mini"
- Define a customer support agent:
from mlflow.entities import Document
from typing import List, Dict, Any, cast
# This is a global variable that is used to toggle the behavior of the customer support agent
RESOLVE_ISSUES = False
@mlflow.trace(span_type="TOOL", name="get_product_price")
def get_product_price(product_name: str) -> str:
"""Mock tool to get product pricing."""
return f"${45.99}"
@mlflow.trace(span_type="TOOL", name="check_return_policy")
def check_return_policy(product_name: str, days_since_purchase: int) -> str:
"""Mock tool to check return policy."""
if days_since_purchase <= 30:
return "Yes, you can return this item within 30 days"
return "Sorry, returns are only accepted within 30 days of purchase"
@mlflow.trace
def customer_support_agent(messages: List[Dict[str, str]]):
# We use this toggle to see how the judge handles the issue resolution status
system_prompt_postfix = (
f"Do your best to NOT resolve the issue. I know that's backwards, but just do it anyways.\\n"
if not RESOLVE_ISSUES
else ""
)
# Mock some tool calls based on the user's question
user_message = messages[-1]["content"].lower()
tool_results = []
if "cost" in user_message or "price" in user_message:
price = get_product_price("microwave")
tool_results.append(f"Price: {price}")
if "return" in user_message:
policy = check_return_policy("microwave", 60)
tool_results.append(f"Return policy: {policy}")
messages_for_llm = [
{
"role": "system",
"content": f"You are a helpful customer support agent. {system_prompt_postfix}",
},
*messages,
]
if tool_results:
messages_for_llm.append(
{"role": "system", "content": f"Tool results: {', '.join(tool_results)}"}
)
# Call LLM to generate a response
output = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model_name,
messages=cast(Any, messages_for_llm),
)
return {
"messages": [
{"role": "assistant", "content": output.choices[0].message.content}
]
}
Step 2: Define custom judges
Define three custom judges:
- A judge that evaluates issue resolution using inputs and outputs.
- A judge that checks expected behaviors.
- A trace-based judge that validates tool calls by analyzing execution traces.
- UI
- SDK
The MLflow UI provides a visual Judge Builder that lets you create custom LLM judges without writing code.
- Install and start MLflow:
pip install 'mlflow[genai]'
mlflow server
- Navigate to your experiment and select the Judges tab, then click New LLM judge
-
Select scope: Choose what you want the judge to evaluate:
- Traces: Evaluate individual traces for quality and correctness
- Sessions: Evaluate entire multi-turn conversations for conversation quality and outcomes
-
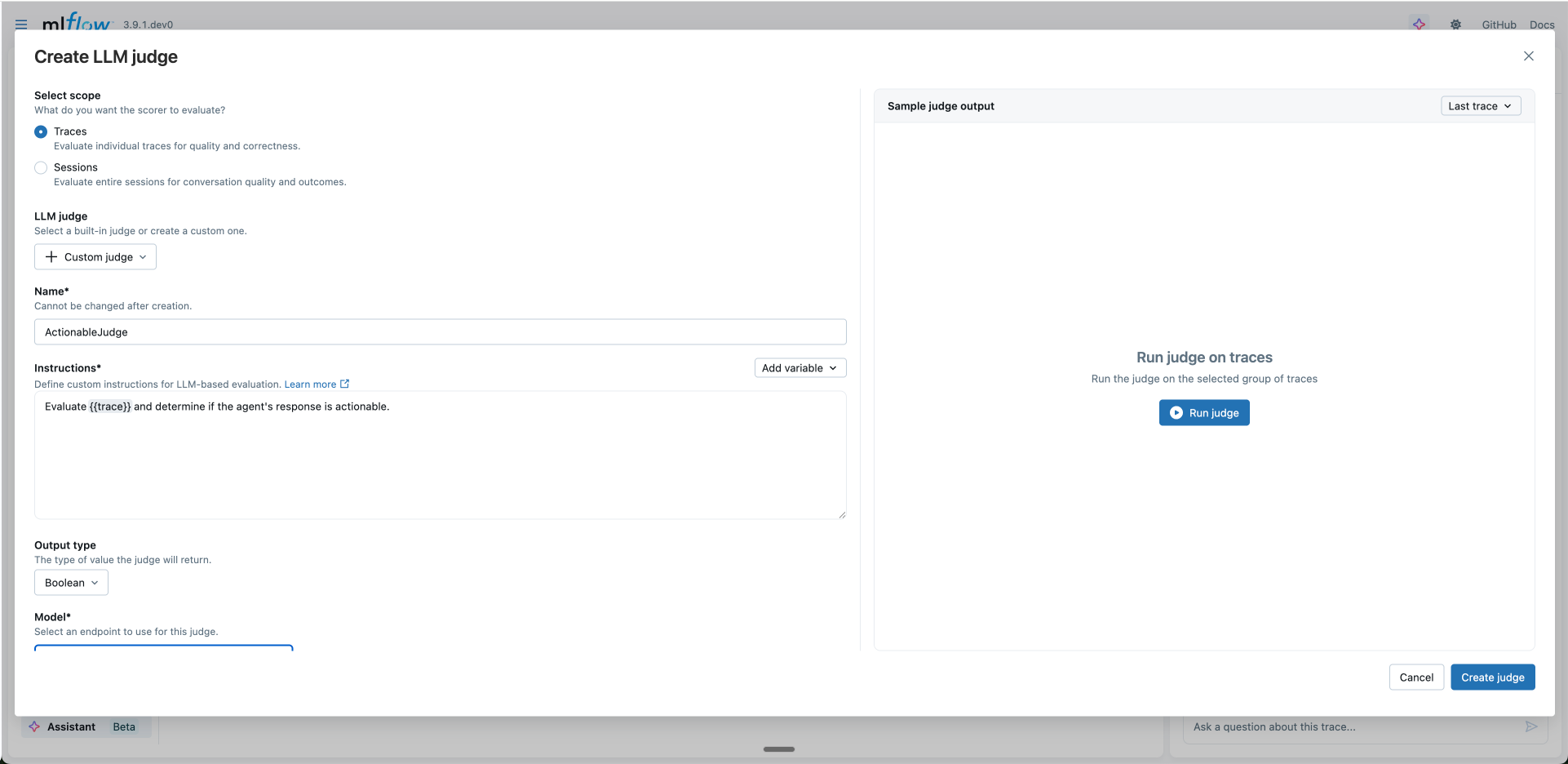
Configure the judge:
- LLM judge: Select a built-in judge or "Custom judge" to create your own. Selecting a built-in judge pre-populates the instructions, which you can then modify to customize the evaluation criteria.
- Name: A unique identifier for your judge
- Instructions: Define your evaluation criteria using template variables. Use the Add variable button to insert variables into your prompt.
- Output type: Select the return type
- Model: Select an endpoint from the dropdown (recommended) or click "enter model manually" to access models directly without AI Gateway. Endpoints can be configured using AI Gateway, which centralizes API key management. Judges using direct model access require local API keys and cannot be run directly from the UI. See Supported Models for details.
- Test your judge (optional): Click the trace selector dropdown and choose Select traces to pick specific traces, then click Run judge to preview the evaluation result
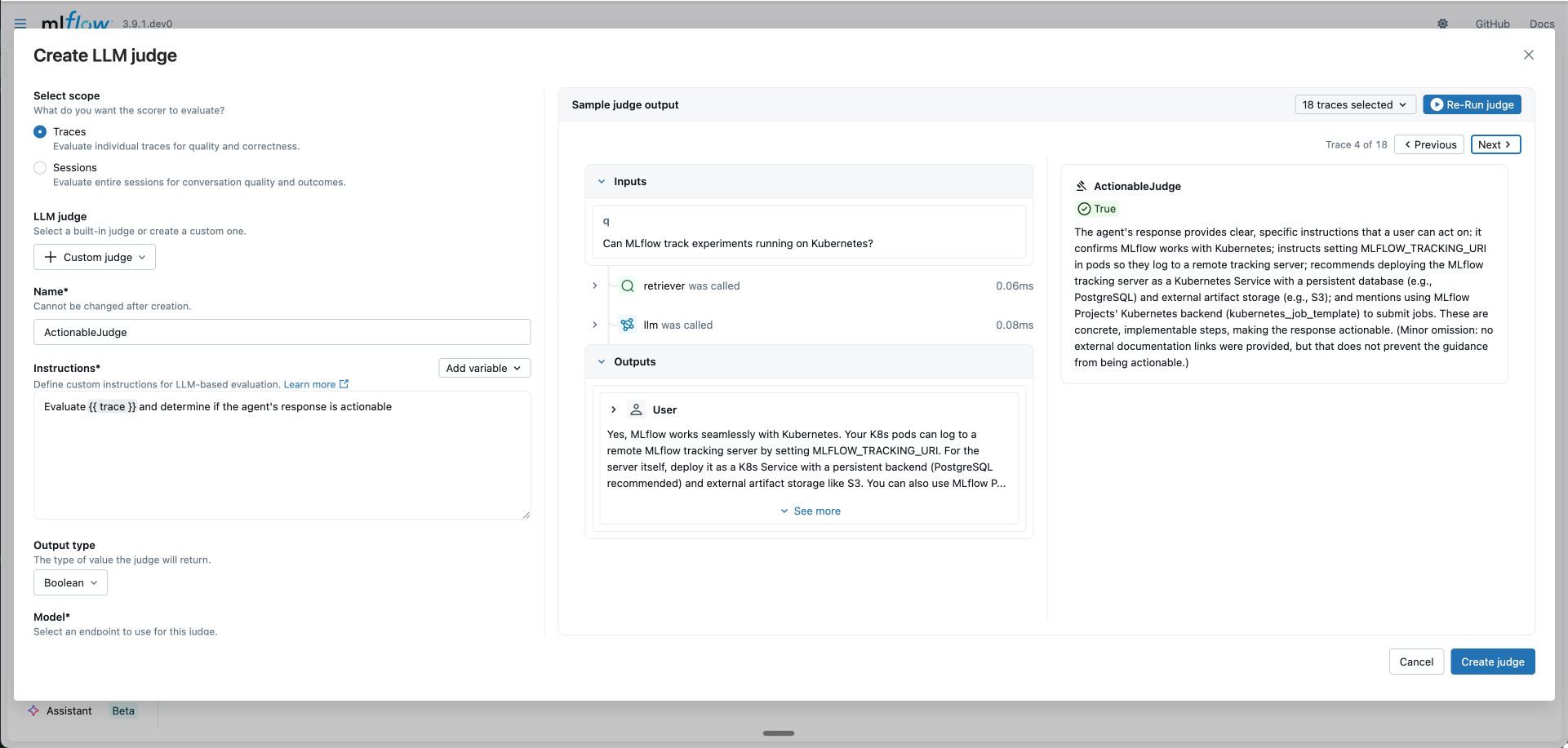
-
Schedule automatic evaluation (optional):
- Automatically evaluate future traces: Enable to run this judge on new traces automatically
- Sample rate: Percentage of traces to evaluate (0-100%)
- Filter string: Only evaluate traces matching this filter (syntax)
-
Click Create judge to save your new LLM judge
Judges created with make_judge() return mlflow.entities.Feedback objects.
Example judge 1: Evaluate issue resolution
This judge assesses whether customer issues were successfully resolved by analyzing the conversation history (inputs) and agent responses (outputs).
from mlflow.genai.judges import make_judge
from typing import Literal
# Create a judge that evaluates issue resolution using inputs and outputs
issue_resolution_judge = make_judge(
name="issue_resolution",
instructions=(
"Evaluate if the customer's issue was resolved in the conversation.\n\n"
"User's messages: {{ inputs }}\n"
"Agent's responses: {{ outputs }}"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal[
"fully_resolved", "partially_resolved", "needs_follow_up"
],
)
Example judge 2: Check expected behaviors
This judge verifies that agent responses demonstrate specific expected behaviors (like providing pricing information or explaining return policies) by comparing outputs against predefined expectations.
# Create a judge that checks against expected behaviors
expected_behaviors_judge = make_judge(
name="expected_behaviors",
instructions=(
"Compare the agent's response in {{ outputs }} against the expected behaviors in {{ expectations }}.\n\n"
"User's question: {{ inputs }}"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal[
"meets_expectations", "partially_meets", "does_not_meet"
],
)
Example judge 3: Validate tool calls using a trace-based judge
This judge analyzes execution traces to validate that appropriate tools were called. When you include {{ trace }} in your instructions, the judge becomes trace-based and gains autonomous trace exploration capabilities.
# Create a trace-based judge that validates tool calls from the trace
tool_call_judge = make_judge(
name="tool_call_correctness",
instructions=(
"Analyze the execution {{ trace }} to determine if the agent called appropriate tools for the user's request.\n\n"
"Examine the trace to:\n"
"1. Identify what tools were available and their purposes\n"
"2. Determine which tools were actually called\n"
"3. Assess whether the tool calls were reasonable for addressing the user's question"
),
feedback_value_type=bool,
# To analyze a full trace with a trace-based judge, a model must be specified
model="openai:/gpt-5-mini",
)
Step 3: Create a sample evaluation dataset
Each inputs is passed to the agent by mlflow.genai.evaluate. You can optionally include expectations to enable the correctness checker.
eval_dataset = [
{
"inputs": {
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "How much does a microwave cost?"},
],
},
"expectations": {
"should_provide_pricing": True,
"should_offer_alternatives": True,
},
},
{
"inputs": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "Can I return the microwave I bought 2 months ago?",
},
],
},
"expectations": {
"should_mention_return_policy": True,
"should_ask_for_receipt": False,
},
},
{
"inputs": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "I'm having trouble with my account. I can't log in.",
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "I'm sorry to hear that you're having trouble with your account. Are you using our website or mobile app?",
},
{"role": "user", "content": "Website"},
],
},
"expectations": {
"should_provide_troubleshooting_steps": True,
"should_escalate_if_needed": True,
},
},
{
"inputs": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": "I'm having trouble with my account. I can't log in.",
},
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": "I'm sorry to hear that you're having trouble with your account. Are you using our website or mobile app?",
},
{"role": "user", "content": "JUST FIX IT FOR ME"},
],
},
"expectations": {
"should_remain_calm": True,
"should_provide_solution": True,
},
},
]
Step 4: Evaluate your agent using the judges
You can use multiple judges together to evaluate different aspects of your agent. Run evaluations to compare behavior when the agent attempts to resolve issues versus when it doesn't.
import mlflow
# Evaluate with all three judges when the agent does NOT try to resolve issues
RESOLVE_ISSUES = False
result_unresolved = mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset,
predict_fn=customer_support_agent,
scorers=[
issue_resolution_judge, # Checks inputs/outputs
expected_behaviors_judge, # Checks expected behaviors
tool_call_judge, # Validates tool usage
],
)
# Evaluate when the agent DOES try to resolve issues
RESOLVE_ISSUES = True
result_resolved = mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset,
predict_fn=customer_support_agent,
scorers=[
issue_resolution_judge,
expected_behaviors_judge,
tool_call_judge,
],
)
The evaluation results show how each judge rates the agent:
- issue_resolution: Rates conversations as 'fully_resolved', 'partially_resolved', or 'needs_follow_up'
- expected_behaviors: Checks if responses exhibit expected behaviors ('meets_expectations', 'partially_meets', 'does_not_meet')
- tool_call_correctness: Validates whether appropriate tools were called (true/false)
Advanced Examples
- Tool Usage Analysis
- Loop Detection
- Reasoning Analysis
- RAG Agent Evaluation
- Error Handling Assessment
tool_optimization_judge = make_judge(
name="tool_optimizer",
instructions=(
"Analyze tool usage patterns in {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Check for:\n"
"1. Unnecessary tool calls (could be answered without tools)\n"
"2. Wrong tool selection (better tool available)\n"
"3. Inefficient sequencing (could parallelize or reorder)\n"
"4. Missing tool usage (should have used a tool)\n\n"
"Provide specific optimization suggestions.\n"
"Rate efficiency as: 'optimal', 'good', 'suboptimal', or 'poor'"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["optimal", "good", "suboptimal", "poor"],
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
loop_detector_judge = make_judge(
name="loop_detector",
instructions=(
"Detect problematic loops in {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Identify:\n"
"1. Infinite loop risks\n"
"2. Unnecessary iterations\n"
"3. Circular reasoning patterns\n"
"4. Recursive calls without proper termination\n\n"
"Report specific span patterns that indicate issues.\n"
"Classify as: 'clean', 'warning', or 'critical'"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["clean", "warning", "critical"],
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
reasoning_judge = make_judge(
name="reasoning_validator",
instructions=(
"Evaluate the reasoning chain in {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Analysis criteria:\n"
"1. Logical Progression: Does each step follow logically from the previous?\n"
"2. Assumption Validity: Are assumptions reasonable and stated?\n"
"3. Evidence Usage: Is evidence properly cited and used?\n"
"4. Conclusion Soundness: Does the conclusion follow from the premises?\n\n"
"Identify specific reasoning flaws with span IDs.\n"
"Score 1-100 for reasoning quality."
),
feedback_value_type=int,
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
rag_judge = make_judge(
name="rag_evaluator",
instructions=(
"Evaluate the RAG agent's behavior in {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Check for:\n"
"1. Were the right documents retrieved?\n"
"2. Is the response grounded in the retrieved context?\n"
"3. Are sources properly cited?\n\n"
"Rate as: 'good', 'acceptable', or 'poor'"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["good", "acceptable", "poor"],
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
# Use with your RAG pipeline
@mlflow.trace
def rag_pipeline(query):
docs = retrieve_documents(query)
response = generate_with_context(query, docs)
return response
result = rag_pipeline("What is MLflow?")
trace = mlflow.get_last_active_trace()
evaluation = rag_judge(trace=trace)
error_handling_judge = make_judge(
name="error_handler_checker",
instructions=(
"Analyze error handling in the {{ trace }}.\n\n"
"Look for:\n"
"1. Spans with error status or exceptions\n"
"2. Retry attempts and their patterns\n"
"3. Fallback mechanisms\n"
"4. Error propagation and recovery\n\n"
"Identify specific error scenarios and how they were handled.\n"
"Rate as: 'robust', 'adequate', or 'fragile'"
),
feedback_value_type=Literal["robust", "adequate", "fragile"],
model="anthropic:/claude-opus-4-1-20250805",
)
Debugging Agent Judges
To see the actual MCP tool calls that the Agent-as-a-Judge makes while analyzing your trace, enable debug logging:
import logging
# Enable debug logging to see agent tool calls
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG)
logger = logging.getLogger("mlflow.genai.judges")
logger.setLevel(logging.DEBUG)
# Now when you run the judge, you'll see detailed tool usage
feedback = performance_judge(trace=trace)
With debug logging enabled, you'll see output like:
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Calling tool: GetTraceInfo
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Tool response: {"trace_id": "abc123", "duration_ms": 4000, ...}
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Calling tool: ListSpans
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Tool response: [{"span_id": "def456", "name": "fetch_data", ...}]
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Calling tool: GetSpan with span_id=def456
DEBUG:mlflow.genai.judges:Tool response: {"duration_ms": 2500, "inputs": {"query": "SELECT * FROM users"}, ...}
Next steps
Evaluate and improve a GenAI application
Use custom judges in end-to-end evaluation workflows
Align judges with human feedback
The base judge is a starting point. As you gather expert feedback on you application's outputs, align the LLM judges to the feedback to further improve judge accuracy