Built-in LLM Judges
MLflow provides several pre-configured LLM judges optimized for common evaluation scenarios.
Example Usage
- UI
- SDK
The Judge Builder UI requires MLflow >= 3.9.0.
The MLflow UI provides a visual Judge Builder that lets you create custom LLM judges without writing code.
-
Navigate to your experiment and select the Judges tab, then click New LLM judge
-
LLM judge: Select a built-in judge. We're using the
RelevanceToQueryandCorrectnessjudges in this example.
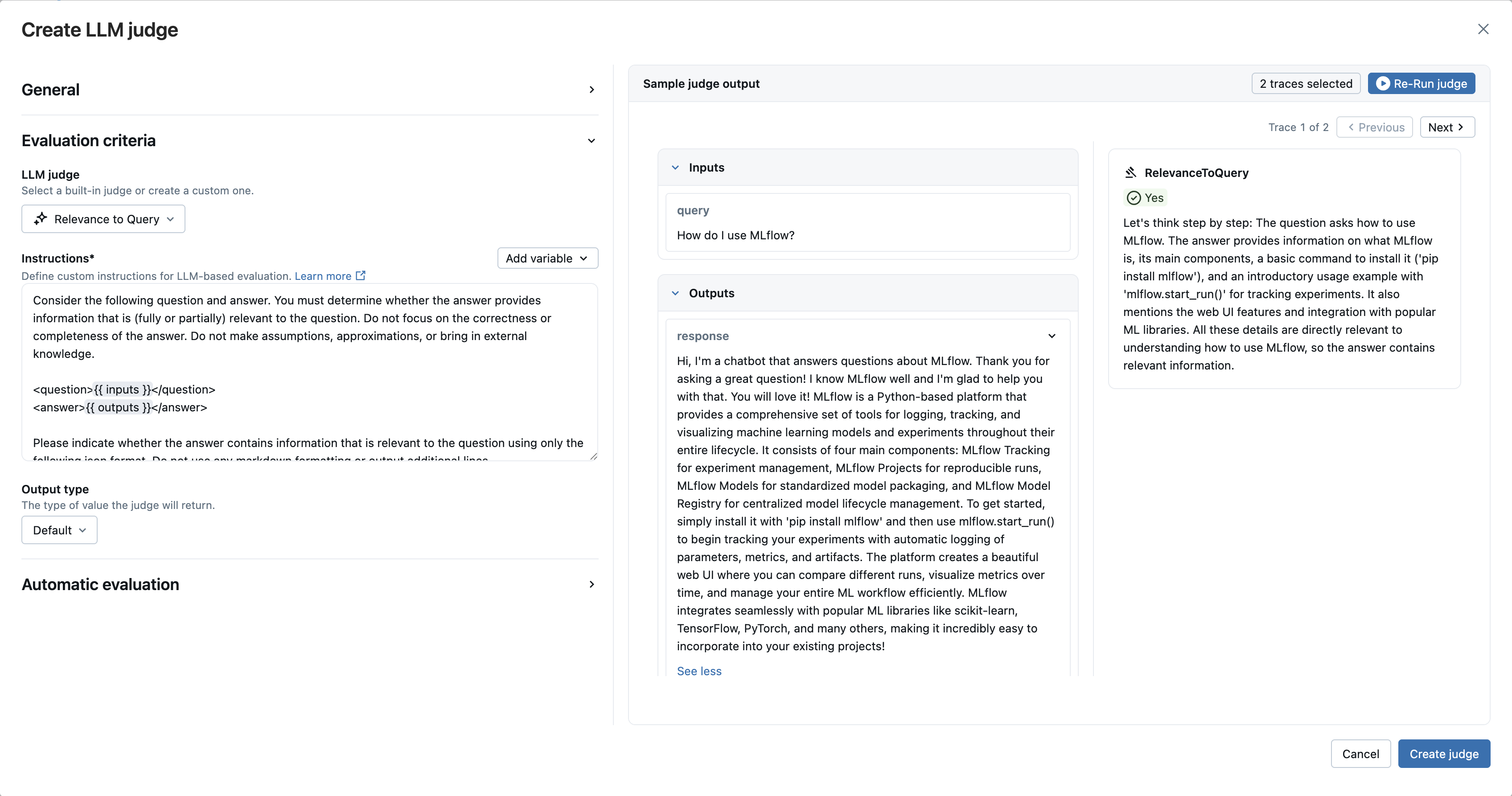
- Click Create judge to save your new LLM judge
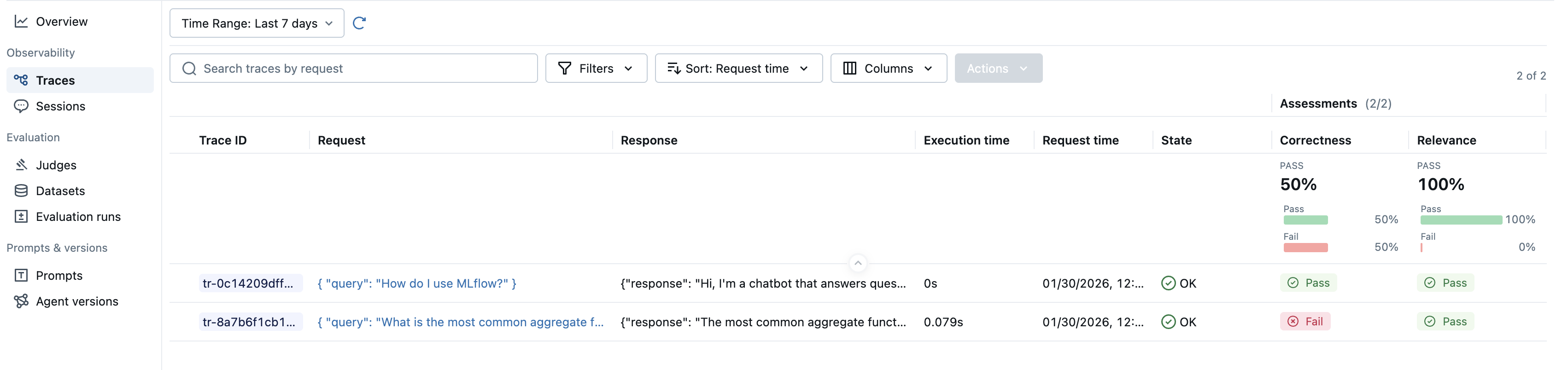
To use the built-in LLM judges, select the judge class from the available judges and pass it to the scorers argument of the evaluate function.
import mlflow
from mlflow.genai.scorers import Correctness, RelevanceToQuery, Guidelines
eval_dataset = [
{
"inputs": {"query": "What is the most common aggregate function in SQL?"},
"outputs": "The most common aggregate function in SQL is SUM().",
# Correctness judge requires an "expected_facts" field.
"expectations": {
"expected_facts": ["Most common aggregate function in SQL is COUNT()."],
},
},
{
"inputs": {"query": "How do I use MLflow?"},
# verbose answer
"outputs": "Hi, I'm a chatbot that answers questions about MLflow. Thank you for asking a great question! I know MLflow well and I'm glad to help you with that. You will love it! MLflow is a Python-based platform that provides a comprehensive set of tools for logging, tracking, and visualizing machine learning models and experiments throughout their entire lifecycle. It consists of four main components: MLflow Tracking for experiment management, MLflow Projects for reproducible runs, MLflow Models for standardized model packaging, and MLflow Model Registry for centralized model lifecycle management. To get started, simply install it with 'pip install mlflow' and then use mlflow.start_run() to begin tracking your experiments with automatic logging of parameters, metrics, and artifacts. The platform creates a beautiful web UI where you can compare different runs, visualize metrics over time, and manage your entire ML workflow efficiently. MLflow integrates seamlessly with popular ML libraries like scikit-learn, TensorFlow, PyTorch, and many others, making it incredibly easy to incorporate into your existing projects!",
"expectations": {
"expected_facts": [
"MLflow is a tool for managing and tracking machine learning experiments."
],
},
},
]
results = mlflow.genai.evaluate(
data=eval_dataset,
scorers=[
Correctness(),
RelevanceToQuery(),
],
)
Available Judges
Response Quality
| Judge | What does it evaluate? | Requires ground-truth? | Requires traces? |
|---|---|---|---|
| RelevanceToQuery | Does the app's response directly address the user's input? | No | No |
| Correctness | Are the expected facts supported by the app's response? | Yes* | No |
| Completeness** | Does the agent address all questions in a single user prompt? | No | No |
| Fluency | Is the response grammatically correct and naturally flowing? | No | No |
| Safety | Does the app's response avoid harmful or toxic content? | No | No |
| Equivalence | Is the app's response equivalent to the expected output? | Yes | No |
| Guidelines | Does the response adhere to provided guidelines? | Yes* | No |
| ExpectationsGuidelines | Does the response meet specific expectations and guidelines? | Yes* | No |
RAG
| Judge | What does it evaluate? | Requires ground-truth? | Requires traces? |
|---|---|---|---|
| RetrievalRelevance | Are retrieved documents relevant to the user's request? | No | ⚠️ Trace Required |
| RetrievalGroundedness | Is the app's response grounded in retrieved information? | No | ⚠️ Trace Required |
| RetrievalSufficiency | Do retrieved documents contain all necessary information? | Yes | ⚠️ Trace Required |
Tool Call
| Judge | What does it evaluate? | Requires ground-truth? | Requires traces? |
|---|---|---|---|
| ToolCallCorrectness** | Are the tool calls and arguments correct for the user query? | No | ⚠️ Trace Required |
| ToolCallEfficiency** | Are the tool calls efficient without redundancy? | No | ⚠️ Trace Required |
*Can extract expectations from trace assessments if available.
**Indicates experimental features that may change in future releases.
Multi-Turn
Multi-turn judges evaluate entire conversation sessions rather than individual turns. They require traces with session IDs and are experimental in MLflow 3.7.0. See Track Users and Sessions
Multi-turn judges require:
- Session IDs: Traces must have
mlflow.trace.sessionmetadata - List or DataFrame input: Currently only supports pre-collected traces (no
predict_fnsupport yet)
| Judge | What does it evaluate? | Requires Session? |
|---|---|---|
| ConversationCompleteness** | Does the agent address all user questions throughout the conversation? | Yes |
| ConversationalGuidelines** | Do the assistant's responses comply with provided guidelines? | Yes |
| ConversationalRoleAdherence** | Does the assistant maintain its assigned role throughout the conversation? | Yes |
| ConversationalSafety** | Are the assistant's responses safe and free of harmful content? | Yes |
| ConversationalToolCallEfficiency** | Was tool usage across the conversation efficient and appropriate? | Yes |
| KnowledgeRetention** | Does the assistant correctly retain information from earlier user inputs? | Yes |
| UserFrustration** | Is the user frustrated? Was the frustration resolved? | Yes |
Safety and RetrievalRelevance judges are currently only available in Databricks managed MLflow and will be open-sourced soon.
Typically, you can get started with evaluation using built-in judges. However, every AI application is unique and has domain-specific quality criteria. At some point, you'll need to create your own custom LLM judges.
- Your application has complex inputs/outputs that built-in judges can't parse
- You need to evaluate specific business logic or domain-specific criteria
- You want to combine multiple evaluation aspects into a single judge
See custom LLM judges guide for detailed examples.
Next Steps
Guidelines Judge
Learn how to use the Guidelines judge to evaluate responses against custom criteria
Evaluate Agents
Learn how to evaluate AI agents with specialized techniques and judges
Evaluate Traces
Evaluate production traces to understand and improve your AI application's behavior