Feedback Concepts
What is Feedback?
Feedback in MLflow represents the result of any quality assessment performed on your GenAI application outputs. It provides a standardized way to capture evaluations, whether they come from automated systems, LLM judges, or human reviewers.
Feedback serves as the bridge between running your application and understanding its quality, enabling you to systematically track performance across different dimensions like correctness, relevance, safety, and adherence to guidelines.
Feedbacks attached to traces
Use Cases
Manual Quality Checks
Manual quality checks are important for ensuring the quality of your GenAI application. For example, you can attach a feedback to indicate the hallucination in the response and compare quality between different models.
End-User Feedbacks
Feedbacks from end-users are precious for improving the quality of your GenAI application. By storing feedbacks on your traces, you can easily monitor the user satisfaction of your application over time.
LLM Judge Evaluation
LLM judges are powerful tools for systematically running quality checks at scale. When using MLflow's GenAI Evaluation, Feedbacks from LLM judges are attached to the traces, enabling you to track evaluation results in the unified way as manual quality checks.
Collaborative Annotation
Quality checks are often performed by multiple annotators to ensure the robustness of the output. MLflow tracks metadata and revision history of the feedbacks and supports aggregation of feedbacks from multiple annotators.
Core Structure
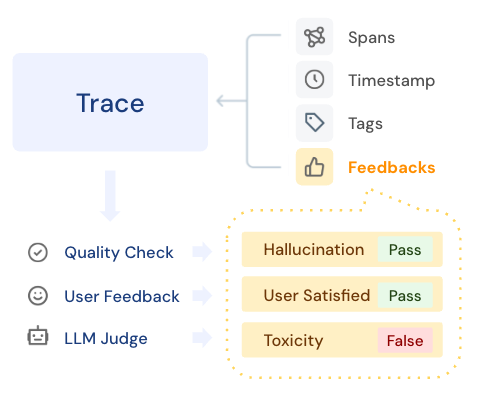
Feedback is often created by different sources, such as human annotators, LLM judges, or real user's feedback in the application. The Feedback object in MLflow is a standard container for storing these signals along with metadata to track
how they are created. Feedbacks are associated with a Trace, or a particular Span in the Trace.
Feedback Object Schema
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
name | str | A string identifying the specific quality aspect being assessed |
value | Any | The actual feedback value, which can be
|
rationale | str | A string explaining why the feedback is given to the trace. |
source | AssessmentSource | The source of the feedback, composed of the type of the source and ID.
|
error | Optional[AssessmentError] | An optional error associated with the feedback. This is used to indicate that the feedback was not processed successfully, for example, an exception from the LLM judge execution. |
metadata | Optional[dict[str, str]] | Optional key-value pairs associated with the feedback. |
create_time_ms | int | The timestamp of when the feedback is created, in milliseconds. |
last_update_time_ms | int | The timestamp of when the feedback is updated, in milliseconds. |
trace_id | str | The ID of the trace that the feedback is attached to. |
span_id | Optional[str] | The ID of the span that the feedback is attached to, if it is associated with a particular span in the trace. For example, you can give a feedback to the specific retriever output in the RAG application. |
Feedback Examples
Human Feedback for Hallucination in the Response
{
"name": "hallucination",
"value": false,
"rationale": "The response is factual and does not contain any hallucinations.",
"source": {
"source_type": "HUMAN",
"source_id": "john@example.com"
}
}
LLM Judge Feedback for Factual Accuracy
{
"name": "factual_accuracy",
"value": 0.85,
"rationale": "The response correctly identifies 3 out of 4 key facts about MLflow, but incorrectly states the founding year.",
"source": {
"source_type": "LLM_JUDGE",
"source_id": "openai:/4o-mini"
},
"metadata": {
# Store link to the prompt used for the judge, registered in MLflow Prompt Registry
"judge_prompt": "prompts:factual_accuracy_judge/1"
}
}
Error Feedback from LLM Judge (Rate Limit Exceeded)
{
"name": "safety",
"error": {
"error_code": "RATE_LIMIT_EXCEEDED",
"error_message": "Rate limit for the judge exceeded.",
"stack_trace": "..."
},
"source": {
"source_type": "LLM_JUDGE",
"source_id": "openai:/4o-mini"
}
}
Next Steps
Feedback Guide
Complete guide for using mlflow.log_feedback with practical examples and code samples
Expectations Concepts
Learn how to define ground truth expectations for comprehensive evaluation
Ground Truth Expectations
Understand how to define expected outputs for comprehensive evaluation