Spans
What is a Span?
The Span object is a fundamental building block in the Trace data model. It is a container for the information about the individual steps of the trace, such as LLM calls, tool execution, retrieval, etc. Spans form a hierarchical tree structure within a single trace, which represents the execution flow of the trace.
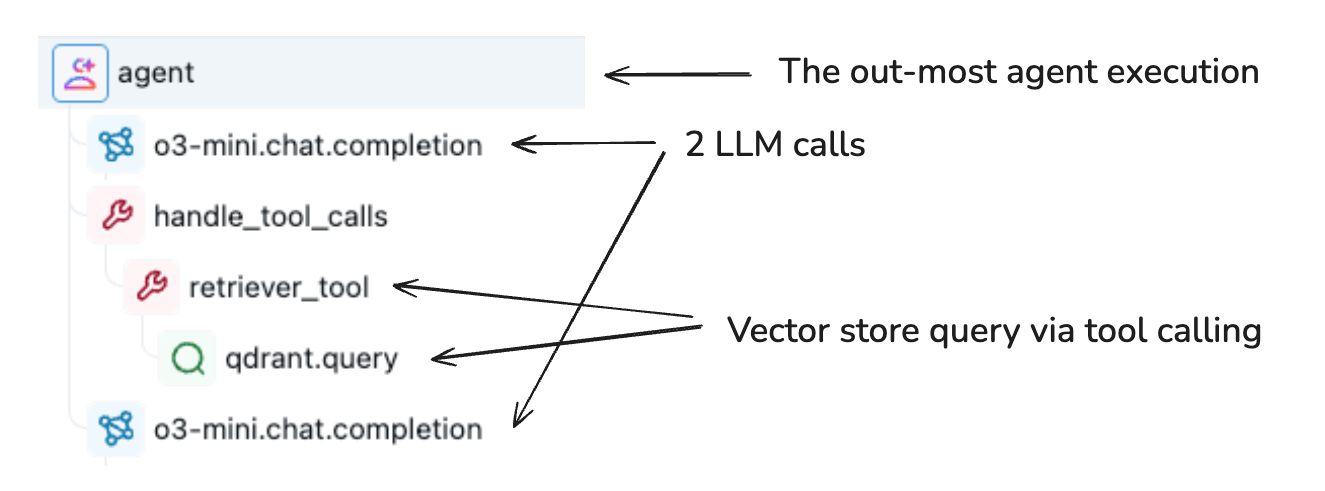
Example of a Span for a Tool Calling Agent
For example, the above picture illustrates a set of spans that are organized in a tree structure in a trace. Each line represents a span, where the tree-structure is formed by the curly edges between lines.
Span Object Schema
MLflow's Span object is designed to be compatible with the OpenTelemetry Span spec. It is a dataclass object that is mostly same as the OpenTelemetry span object, but with some additional convenience accessors and methods to support GenAI use cases. When exported to OpenTelemetry-compatible backend, the Span object is serialized into the strict OpenTelemetry export format (OTLP).
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
span_id | str | A unique identifier that is generated for each span within a trace. |
trace_id | str | The unique identifier that links this span to its parent trace. |
parent_id | Optional[str] | The identifier that establishes the hierarchical association of a given span with its parent span. If the span is the root span, this field is None. |
name | str | The name of the span, either user-defined or automatically generated based on the function or method being instrumented. |
start_time_ns | int | The unix timestamp (in nanoseconds) when the span was started. |
end_time_ns | int | The unix timestamp (in nanoseconds) when the span was ended. |
status | SpanStatus | The status of a span with values of OK, UNSET, or ERROR. The span status object contains an optional description if the status_code is reflecting an error that occurred. |
inputs | Optional[Any] | The input data that is passed into the particular stage of your application. |
outputs | Optional[Any] | The output data that is passed out of the particular stage of your application. |
attributes | Dict[str, Any] | Attributes are metadata that are associated with a given step within your application. These are key-value pairs that provide insight into behavioral modifications for function and method calls. |
events | List[SpanEvent] | Events are a system-level property that is optionally applied to a span only if there was an issue during the execution of the span. These events contain information about exceptions that were thrown in the instrumented call, as well as the stack trace. |
Span Attributes
Span attributes are key-value pairs that provide insight into behavioral modifications for function and method calls.
span.set_attributes(
{
"ai.model.name": "o3-mini",
"ai.model.version": "2024-01-01",
"ai.model.provider": "openai",
"ai.model.temperature": 0.7,
"ai.model.max_tokens": 1000,
"infrastructure.gpu.type": "A100",
"infrastructure.memory.used_mb": 2048,
}
)
Span Types
Span types are a way to categorize spans within a trace. MLflow provides a set of predefined span types for common use cases, while also allowing you to set custom span types.
- Built-in Types
- Setting Span Types
- Search Spans by Type
| Span Type | Description |
|---|---|
"CHAT_MODEL" | Represents a query to a chat model. This is a special case of an LLM interaction. |
"CHAIN" | Represents a chain of operations. |
"AGENT" | Represents an autonomous agent operation. |
"TOOL" | Represents a tool execution (typically by an agent), such as querying a search engine. |
"EMBEDDING" | Represents a text embedding operation. |
"RETRIEVER" | Represents a context retrieval operation, such as querying a vector database. |
"PARSER" | Represents a parsing operation, transforming text into a structured format. |
"RERANKER" | Represents a re-ranking operation, ordering the retrieved contexts based on relevance. |
"MEMORY" | Represents a memory operation, such as persisting context in a long-term memory db. |
"UNKNOWN" | A default span type that is used when no other span type is specified. |
When you are using automatic tracing, the span type is automatically set by MLflow.
To set a span type for manually created spans, you can pass the span_type parameter to the mlflow.trace() decorator or mlflow.start_span() context manager. When you are using automatic tracing, the span type is automatically set by MLflow.
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
# Setting a span type with the decorator
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.RETRIEVER)
def retrieve_documents(query: str):
...
# Setting a span type with the context manager
with mlflow.start_span(name="add", span_type=SpanType.TOOL) as span:
span.set_inputs({"x": x, "y": y})
z = x + y
span.set_outputs({"z": z})
# You can also define a custom span type string
@mlflow.trace(span_type="ROUTER")
def route_request(request):
...
Span type is useful for searching and filtering particular spans in a large trace. MLflow supports both UI and programmatic span search by span type.
Searching spans by SDK:
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
trace = mlflow.get_trace("<trace_id>")
retriever_spans = trace.search_spans(span_type=SpanType.RETRIEVER)
Searching spans on UI:
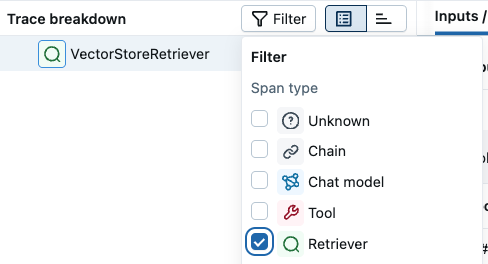
Specialized Span Schemas
MLflow has predefined types of spans, and certain span types have properties that are required in order to enable additional functionality within the UI and downstream tasks such as evaluation.
Retriever Spans
The RETRIEVER span type is used for operations involving retrieving data from a data store (for example, querying documents from a vector store). The output of a RETRIEVER span is expected to be a list of documents.
Each document in the list should be a dictionary with the following structure:
page_content (str): The text content of the retrieved document chunk.
metadata (Optional[Dict[str, Any]]): A dictionary of additional metadata associated with the document. MLflow UI and evaluation metrics may specifically look for:
doc_uri(str): A string URI for the document sourcechunk_id(str): A string identifier if the document is part of a larger chunked document
id (Optional[str]): An optional unique identifier for the document chunk itself.
Example Usage
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities import SpanType, Document
def search_store(query: str) -> list[tuple[str, str]]:
# Simulate retrieving documents (e.g., from a vector database)
return [
(
"MLflow Tracing helps debug GenAI applications...",
"docs/mlflow/tracing_intro.md",
),
(
"Key components of a trace include spans...",
"docs/mlflow/tracing_datamodel.md",
),
("MLflow provides automatic instrumentation...", "docs/mlflow/auto_trace.md"),
]
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.RETRIEVER)
def retrieve_relevant_documents(query: str):
# Get documents from the search store
docs = search_store(query)
# Get the current active span (created by @mlflow.trace)
span = mlflow.get_current_active_span()
# Set the outputs of the span in accordance with the tracing schema
outputs = [
Document(page_content=doc, metadata={"doc_uri": uri}) for doc, uri in docs
]
span.set_outputs(outputs)
# Return the original format for downstream usage
return docs
# Example usage
user_query = "MLflow Tracing benefits"
retrieved_docs = retrieve_relevant_documents(user_query)