Tracing Anthropic
MLflow Tracing provides automatic tracing capability for Anthropic LLMs. By enabling auto tracing
for Anthropic by calling the mlflow.anthropic.autolog() function, MLflow will capture nested traces and log them to the active MLflow Experiment upon invocation of Anthropic Python SDK.
MLflow trace automatically captures the following information about Anthropic calls:
- Prompts and completion responses
- Latencies
- Model name
- Additional metadata such as
temperature,max_tokens, if specified. - Function calling if returned in the response
- Token usage information
- Any exception if raised
- and more...
Getting Started
Install Dependencies
- Python
- JS / TS
pip install 'mlflow[genai]' anthropic
npm install mlflow-anthropic @anthropic-ai/sdk
Start MLflow Server
- Local (pip)
- Local (docker)
If you have a local Python environment >= 3.10, you can start the MLflow server locally using the mlflow CLI command.
mlflow server
MLflow also provides a Docker Compose file to start a local MLflow server with a postgres database and a minio server.
git clone --depth 1 --filter=blob:none --sparse https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow.git
cd mlflow
git sparse-checkout set docker-compose
cd docker-compose
cp .env.dev.example .env
docker compose up -d
Refer to the instruction for more details, e.g., overriding the default environment variables.
Enable Tracing and Make API Calls
- Chat Completion API
- JS / TS
Enable tracing with mlflow.anthropic.autolog() and make API calls as usual.
import anthropic
import mlflow
# Enable auto-tracing for Anthropic
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
# Set a tracking URI and an experiment
mlflow.set_tracking_uri("http://localhost:5000")
mlflow.set_experiment("Anthropic")
# Invoke the Anthropic model as usual.
# Make sure your API key is set via the ANTHROPIC_API_KEY environment variable.
client = anthropic.Anthropic()
message = client.messages.create(
model="claude-sonnet-4-5-2025092",
max_tokens=512,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude"},
],
)
Wrap the Anthropic client with the tracedAnthropic function and make API calls as usual.
import Anthropic from "@anthropic-ai/sdk";
import { tracedAnthropic } from "mlflow-anthropic";
// Wrap the Anthropic client with the tracedAnthropic function
const client = tracedAnthropic(new Anthropic());
// Invoke the client as usual
const message = await client.messages.create({
model: "claude-3-7-sonnet-20250219",
max_tokens: 512,
messages: [
{ role: "user", content: "Hello, Claude" },
],
});
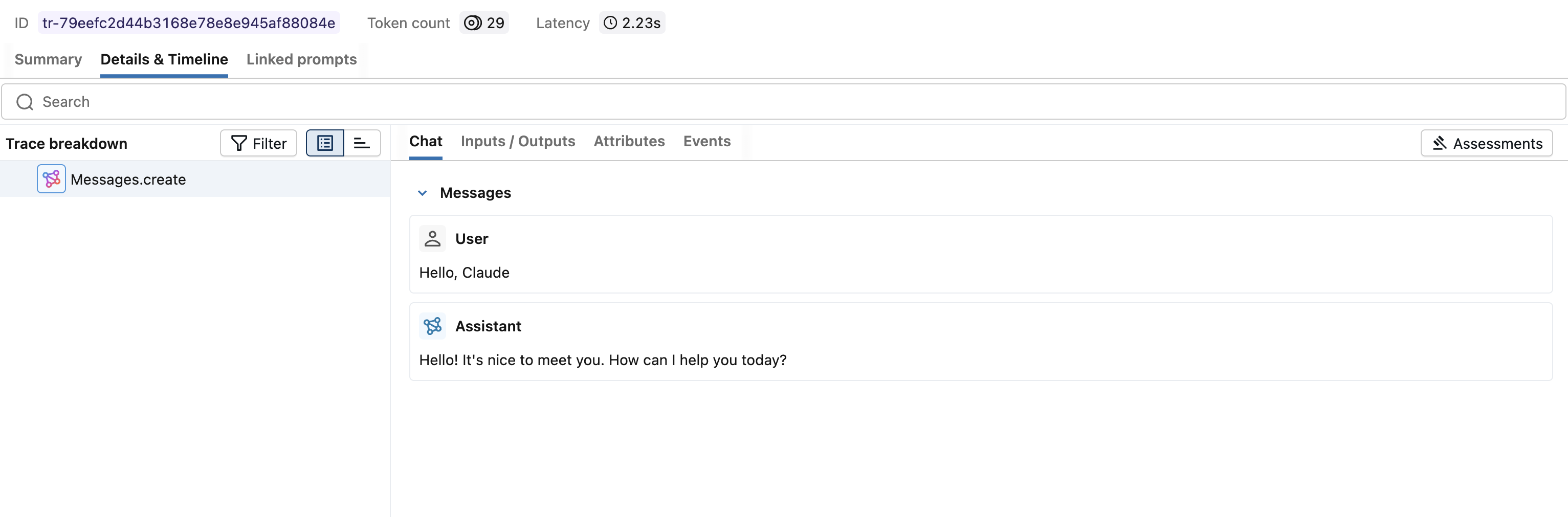
View Traces in MLflow UI
Browse to the MLflow UI at http://localhost:5000 (or your MLflow server URL) and you should see the traces for the Anthropic API calls.
Supported APIs
MLflow supports automatic tracing for the following Anthropic APIs:
| Chat Completion | Function Calling | Streaming | Async | Image | Batch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | - | ✅ (*1) | - | - |
(*1) Async support was added in MLflow 2.21.0.
To request support for additional APIs, please open a feature request on GitHub.
Async
MLflow Tracing has supported the asynchronous API of the Anthropic SDK since MLflow 2.21.0. Its usage is the same as the synchronous API.
- Python
- JS / TS
import anthropic
# Enable trace logging
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
response = await client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[
{"role": "user", "content": "Hello, Claude"},
],
)
Anthropic Typescript / Javascript SDK is natively async. See the Getting Started example above.
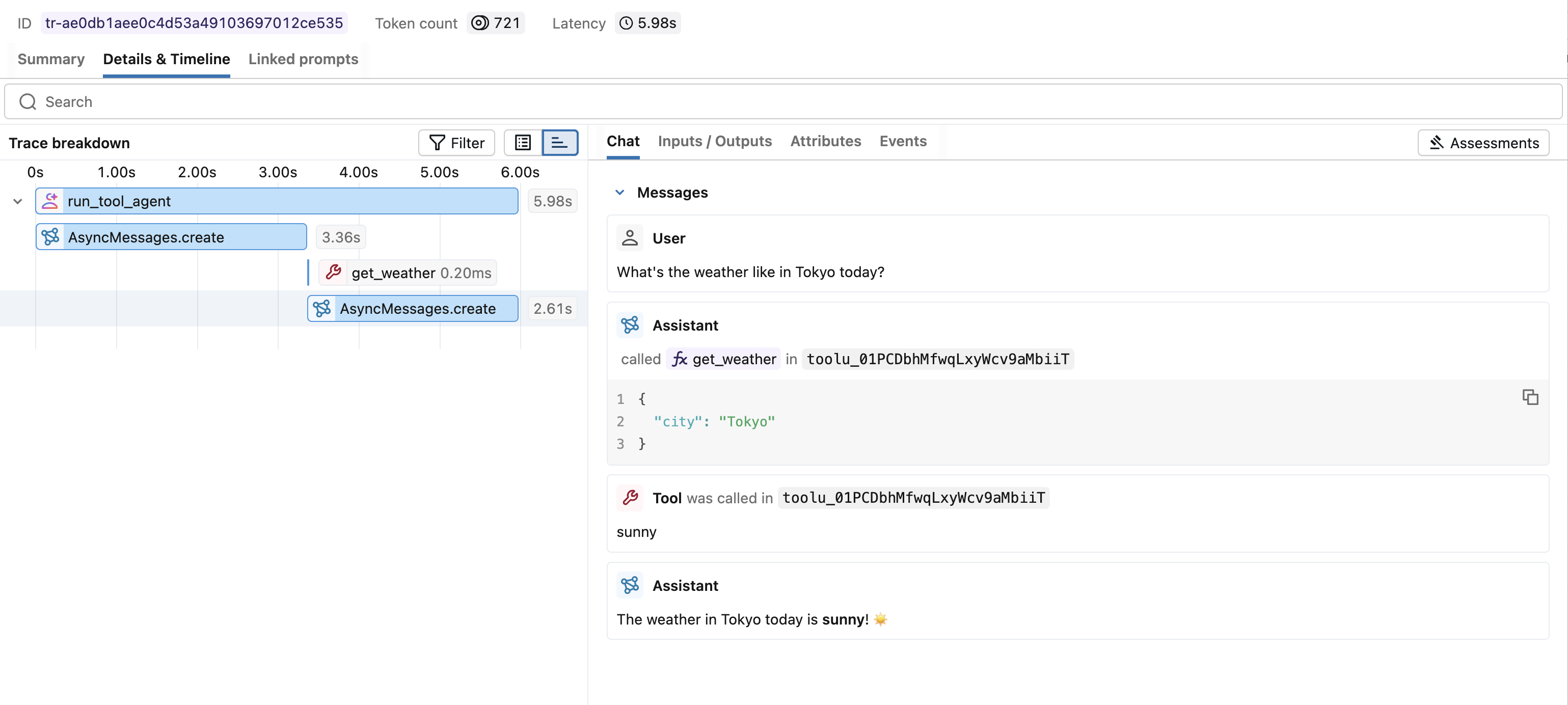
Advanced Example: Tool Calling Agent
MLflow Tracing automatically captures tool calling response from Anthropic models. The function instruction in the response will be highlighted in the trace UI. Moreover, you can annotate the tool function with the @mlflow.trace decorator to create a span for the tool execution.
The following example implements a simple function calling agent using Anthropic Tool Calling and MLflow Tracing for Anthropic. The example further uses the asynchronous Anthropic SDK so that the agent can handle concurrent invocations without blocking.
import json
import anthropic
import mlflow
import asyncio
from mlflow.entities import SpanType
client = anthropic.AsyncAnthropic()
model_name = "claude-sonnet-4-5-20250929"
# Define the tool function. Decorate it with `@mlflow.trace` to create a span for its execution.
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.TOOL)
async def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
if city == "Tokyo":
return "sunny"
elif city == "Paris":
return "rainy"
return "unknown"
tools = [
{
"name": "get_weather",
"description": "Returns the weather condition of a given city.",
"input_schema": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {"city": {"type": "string"}},
"required": ["city"],
},
}
]
_tool_functions = {"get_weather": get_weather}
# Define a simple tool calling agent
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.AGENT)
async def run_tool_agent(question: str):
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": question}]
# Invoke the model with the given question and available tools
ai_msg = await client.messages.create(
model=model_name,
messages=messages,
tools=tools,
max_tokens=2048,
)
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": ai_msg.content})
# If the model requests tool call(s), invoke the function with the specified arguments
tool_calls = [c for c in ai_msg.content if c.type == "tool_use"]
for tool_call in tool_calls:
if tool_func := _tool_functions.get(tool_call.name):
tool_result = await tool_func(**tool_call.input)
else:
raise RuntimeError("An invalid tool is returned from the assistant!")
messages.append(
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "tool_result",
"tool_use_id": tool_call.id,
"content": tool_result,
}
],
}
)
# Send the tool results to the model and get a new response
response = await client.messages.create(
model=model_name,
messages=messages,
max_tokens=2048,
)
return response.content[-1].text
# Run the tool calling agent
cities = ["Tokyo", "Paris", "Sydney"]
questions = [f"What's the weather like in {city} today?" for city in cities]
answers = await asyncio.gather(*(run_tool_agent(q) for q in questions))
for city, answer in zip(cities, answers):
print(f"{city}: {answer}")
Token usage
MLflow >= 3.2.0 supports token usage tracking for Anthropic. The token usage for each LLM call will be logged in the mlflow.chat.tokenUsage attribute. The total token usage throughout the trace will be
available in the token_usage field of the trace info object.
- Python
- JS / TS
import json
import anthropic
import mlflow
mlflow.anthropic.autolog()
client = anthropic.Anthropic()
message = client.messages.create(
model="claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022",
max_tokens=1024,
messages=[{"role": "user", "content": "Hello"}],
)
# Get the trace object just created
last_trace_id = mlflow.get_last_active_trace_id()
trace = mlflow.get_trace(trace_id=last_trace_id)
# Print the token usage
total_usage = trace.info.token_usage
print("== Total token usage: ==")
print(f" Input tokens: {total_usage['input_tokens']}")
print(f" Output tokens: {total_usage['output_tokens']}")
print(f" Total tokens: {total_usage['total_tokens']}")
# Print the token usage for each LLM call
print("\n== Detailed usage for each LLM call: ==")
for span in trace.data.spans:
if usage := span.get_attribute("mlflow.chat.tokenUsage"):
print(f"{span.name}:")
print(f" Input tokens: {usage['input_tokens']}")
print(f" Output tokens: {usage['output_tokens']}")
print(f" Total tokens: {usage['total_tokens']}")
import * as mlflow from "mlflow-tracing";
// After your Anthropic call completes, flush and fetch the trace
await mlflow.flushTraces();
const lastTraceId = mlflow.getLastActiveTraceId();
if (lastTraceId) {
const client = new mlflow.MlflowClient({ trackingUri: "http://localhost:5000" });
const trace = await client.getTrace(lastTraceId);
// Total token usage on the trace
console.log("== Total token usage: ==");
console.log(trace.info.tokenUsage); // { input_tokens, output_tokens, total_tokens }
// Per-span usage (if provided by the provider)
console.log("\n== Detailed usage for each LLM call: ==");
for (const span of trace.data.spans) {
const usage = span.attributes?.["mlflow.chat.tokenUsage"];
if (usage) {
console.log(`${span.name}:`, usage);
}
}
}
== Total token usage: ==
Input tokens: 8
Output tokens: 12
Total tokens: 20
== Detailed usage for each LLM call: ==
Messages.create:
Input tokens: 8
Output tokens: 12
Total tokens: 20
Supported APIs:
Token usage tracking is supported for the following Anthropic APIs:
| Chat Completion | Function Calling | Streaming | Async | Image | Batch |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ✅ | ✅ | - | ✅ (*1) | - | - |
(*1) Async support was added in MLflow 2.21.0.
Disable auto-tracing
Auto tracing for Anthropic can be disabled globally by calling mlflow.anthropic.autolog(disable=True) or mlflow.autolog(disable=True).
Next steps
Track User Feedback
Record user feedback on traces for tracking user satisfaction.
Manage Prompts
Learn how to manage prompts with MLflow's prompt registry.
Evaluate Traces
Evaluate traces with LLM judges to understand and improve your AI application's behavior.