Redacting Sensitive Data from Traces
Traces capture powerful insights for debugging and monitoring your application, however, they may contain sensitive data, such as Personal Identifiable Information (PII), that you don't want to share with others. MLflow provides a fully configurable way to mask sensitive data from traces before they are saved to the backend.
How It Works
MLflow allows you to configure a list of post-processing hooks that are applied to each span in a trace. Each span processor is a function that takes a span as input and updates it in place.
- Define a custom filtering function and call
mlflow.tracing.configureto register it. - Whenever a new span is created, the registered filters are applied to it sequentially.
- MLflow sends the filtered span to the backend.
Since the filters are applied at client side before sending the span to the backend, the sensitive data never goes out of your application.
Filtering Function
A filtering function must take a single argument, which is a Span object. It can mutate the span in-place. It must not return a value.
def filter_function(span: Span) -> None:
...
Example 1: Redacting E-mail Address
In this example, we'll redact the e-mail address from the user inputs using a simple regex.
import re
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities.span import Span
# Your application code (simplified)
@mlflow.trace
def predict(text: str):
return "Answer"
# Regex pattern to match e-mail addresses
EMAIL_PATTERN = r"[A-Za-z0-9._%+-]+@[A-Za-z0-9.-]+\.[A-Za-z]{2,}"
# Define a filtering function that takes a span as input and mutates it in-place.
def redact_email(span: Span) -> None:
raw_input = span.inputs.get("text")
redacted_input = re.sub(EMAIL_PATTERN, "[REDACTED]", raw_input)
span.set_inputs({"text": redacted_input})
# Register the filter function
mlflow.tracing.configure(span_processors=[redact_email])
# Run the application
predict("My e-mail address is test@example.com")
The generated trace will have the e-mail address redacted in the inputs:

Example 2: Applying a Filter to Particular Spans
The filtering function registered at mlflow.tracing.configure is applied to all spans. If your trace contains many nested spans, you may want to apply the filter only to certain spans. Also, the input/output format is typically different for different span types, so you may need to apply different filtering logic.
In the following example, we'll redact the bank account number from the trace, but using different filtering logic depending on the span type.
First, let's define a simple tool calling agent.
import mlflow
from langchain_core.tools import tool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langgraph.prebuilt import create_react_agent
# Enabling tracing for LangGraph
mlflow.langchain.autolog()
@tool
def get_bank_account_number(user_name: str):
"""Return the bank account number for the given user name."""
return "1234567890"
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="o4-mini")
tools = [get_bank_account_number]
graph = create_react_agent(llm, tools)
Then, let's define a filtering function. By checking the span_type field, we can apply different filtering logic to different span types.
import re
from typing import Union
from mlflow.entities.span import Span, SpanType
ACCOUNT_NUMBER_PATTERN = re.compile(r"\d{10}")
def filter_bank_account_number(span: Span) -> None:
# Redact the output of the tool call span.
if span.span_type == SpanType.TOOL:
span.set_outputs("[REDACTED]")
return
# Redact the back account number from other spans.
if isinstance(span.inputs, dict) and (messages := span.inputs.get("messages")):
span.set_inputs({"messages": redact_messages(messages)})
if isinstance(span.outputs, dict) and (messages := span.outputs.get("messages")):
span.set_outputs({"messages": redact_messages(messages)})
def redact_messages(messages: list[dict]):
if isinstance(messages, dict):
messages = messages.get("messages")
return [
{**msg, "content": ACCOUNT_NUMBER_PATTERN.sub("[REDACTED]", msg["content"])}
for msg in messages
]
Now, let's register the filter function and run the application.
# Register the filter function
mlflow.tracing.configure(span_processors=[filter_bank_account_number])
# Run the application
result = graph.invoke(
{
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "What is the bank account number for John Doe?"}
]
}
)
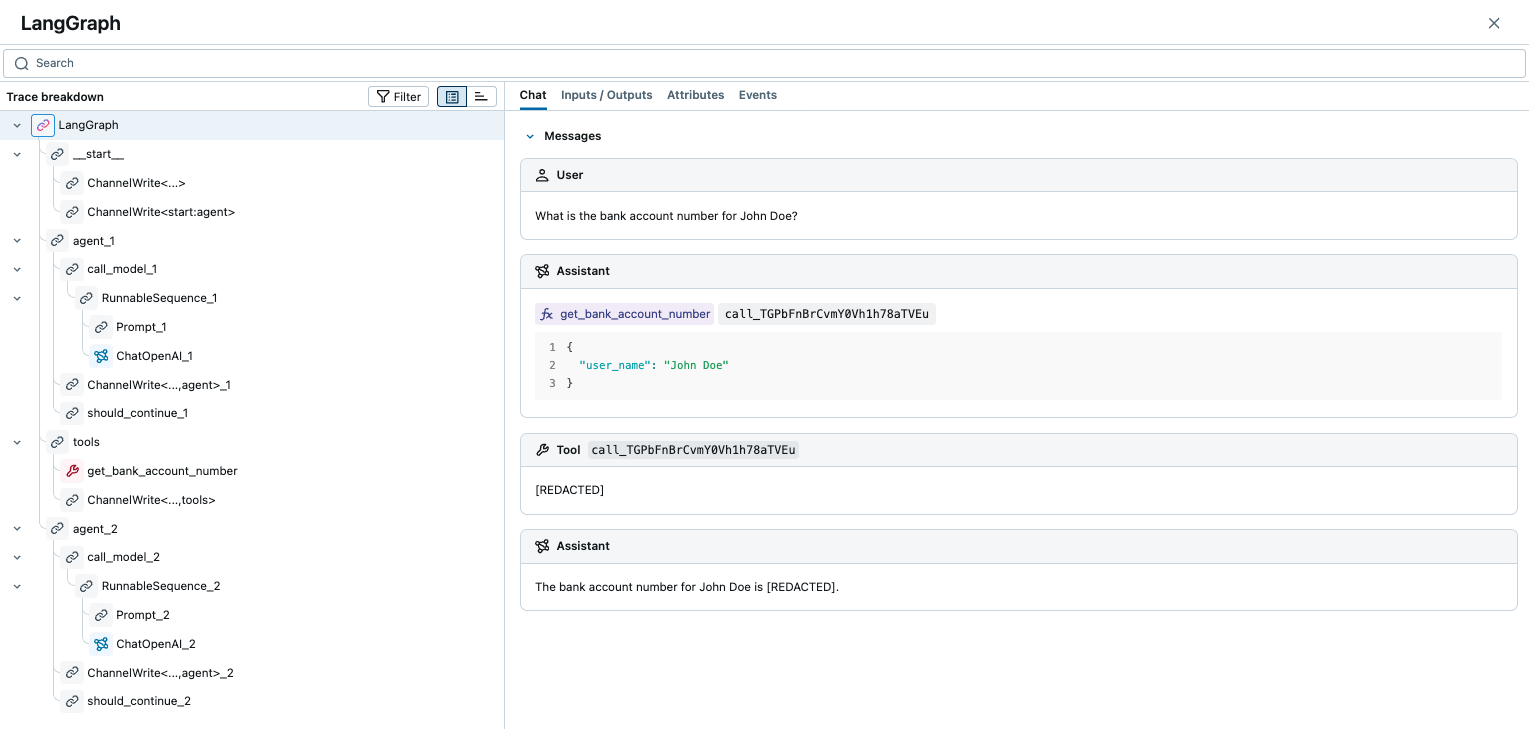
The generated trace will have the bank account number redacted from all messages:
Example 3: Redacting PII using Microsoft Presidio
To go beyond the simple Regex-based filtering, you can use a more sophisticated PII anonymizer such as Microsoft Presidio.
In this example, we run a dummy custom support agent that takes user request such as "I want to cancel my credit card 4095-2609-9393-4932". The request contains many forms of sensitive data such as credit card number, user name, email address, and covering all of them using regex is not trivial.
import mlflow
from mlflow.entities.span import Span, SpanType
# Dummy application code for custom support agent.
@mlflow.trace(span_type=SpanType.AGENT)
def customer_support_agent(request: str):
return "Yes"
With MLflow, plugging in Presidio for filtering sensitive data from traces is straightforward.
First, install Presidio and download the classifier:
pip install presidio_analyzer presidio_anonymizer
python -m spacy download en_core_web_lg
Then, define a filter function that runs Presidio's analyzer and anonymizer on the span input.
from presidio_anonymizer import AnonymizerEngine
from presidio_anonymizer.entities import RecognizerResult, OperatorConfig
# Initialize the anonymizer and analyzer.
anonymizer = AnonymizerEngine()
analyzer = AnalyzerEngine()
# Define a filter function.
def filter_pii(span: Span) -> None:
"""Filter PII from the span input using Microsoft Presidio."""
text = span.inputs.get("request")
results = analyzer.analyze(
text=text,
entities=["PERSON", "CREDIT_CARD", "EMAIL_ADDRESS", "LOCATION", "DATE_TIME"],
language="en",
)
anonymized_text = anonymizer.anonymize(text=text, analyzer_results=results)
span.set_inputs({"request": anonymized_text.text})
Finally, let's register the filter function and run the application.
# Register the filter function
mlflow.tracing.configure(span_processors=[filter_pii])
# Run the application
customer_support_agent(
"Please cancel my credit card effective September 19th. My name is John Doe and my credit "
"card number is 4095-2609-9393-4932. My email is john.doe@example.com and I live in Amsterdam."
)
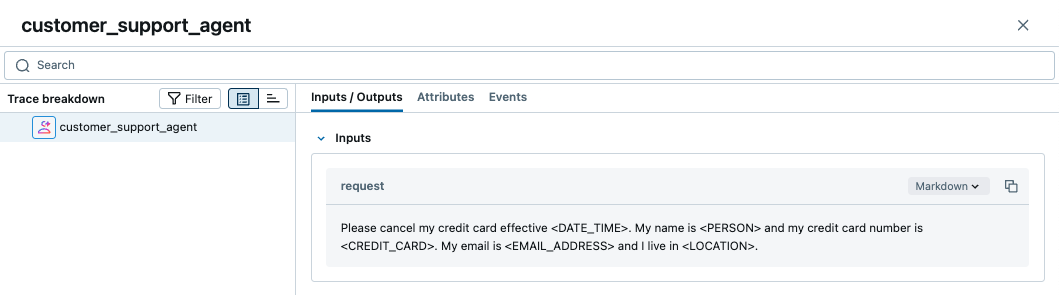
The generated trace will have the PII redacted:
Resetting the Filter
To reset the filter, call mlflow.tracing.configure with an empty list of span processors.
mlflow.tracing.configure(span_processors=[])
Alternatively, you can call mlflow.tracing.reset to reset the entire tracing configuration.
mlflow.tracing.reset()