Deep Learning
The realm of deep learning has witnessed an unprecedented surge, revolutionizing numerous sectors with its ability to process vast amounts of data and capture intricate patterns. From the real-time object detection in autonomous vehicles to the generation of art through Generative Adversarial Networks, and from natural language processing applications in chatbots to predictive analytics in e-commerce, deep learning models are at the forefront of today’s AI-driven innovations.
In the deep learning realm, libraries such as PyTorch, Keras, Tensorflow provide handy tools to build and train deep learning models. MLflow, on the other hand, targets the problem of experiment tracking in deep learning, including logging your experiment setup (learning rate, batch size, etc) along with training metrics (loss, accuracy, etc) and the model (architecture, weights, etc). MLflow provides native integrations with deep learning libraries, so you can plug MLflow into your existing deep learning workflow with minimal changes to your code, and view your experiments in the MLflow UI.
Why MLflow for Deep Learning?
MLflow offers a list of features that power your deep learning workflows:
Experiments Tracking: MLflow tracks your deep learning experiments, including parameters, metrics, and models. Your experiments will be stored in the MLflow server, so you can compare across different experiments and share them.
Model Registry: You can register your trained deep learning models in the MLflow server, so you can easily retrieve them later for inference.
Model Deployment: After training, you can serve the trained model with MLflow as a REST API endpoint, so you can easily integrate it with your application.
Experiments Tracking
Tracking is the cornerstone of the MLflow ecosystem, and especially vital for the iterative nature of deep learning:
Experiments and Runs: Organize your deep learning projects into experiments, with each experiment containing multiple runs. Each run captures essential data like metrics at various training steps, hyperparameters, and the code state.
Artifacts: Store vital outputs such as deep learning models, visualizations, or even tensorboard logs. This artifact repository ensures traceability and easy access.
Metrics at Steps: With deep learning’s iterative nature, MLflow allows logging metrics at various training steps, offering a granular view of the model’s progress.
Dependencies and Environment: Capture the computational environment, including deep learning frameworks’ versions, ensuring reproducibility.
Input Examples and Model Signatures: Define the expected format of the model’s inputs, crucial for complex data like images or sequences.
UI Integration: The enhanced UI provides a visual overview of deep learning runs, facilitating comparison and insights into training progress.
Search Functionality: Efficiently navigate through your deep learning experiments using robust search capabilities.
APIs: Interact with the tracking system programmatically, integrating deep learning workflows seamlessly.
Easier DL Model Comparison with Charts
Use charts to compare deep learning (DL) model training convergence easily. Quickly identify superior configuration sets across training iterations.
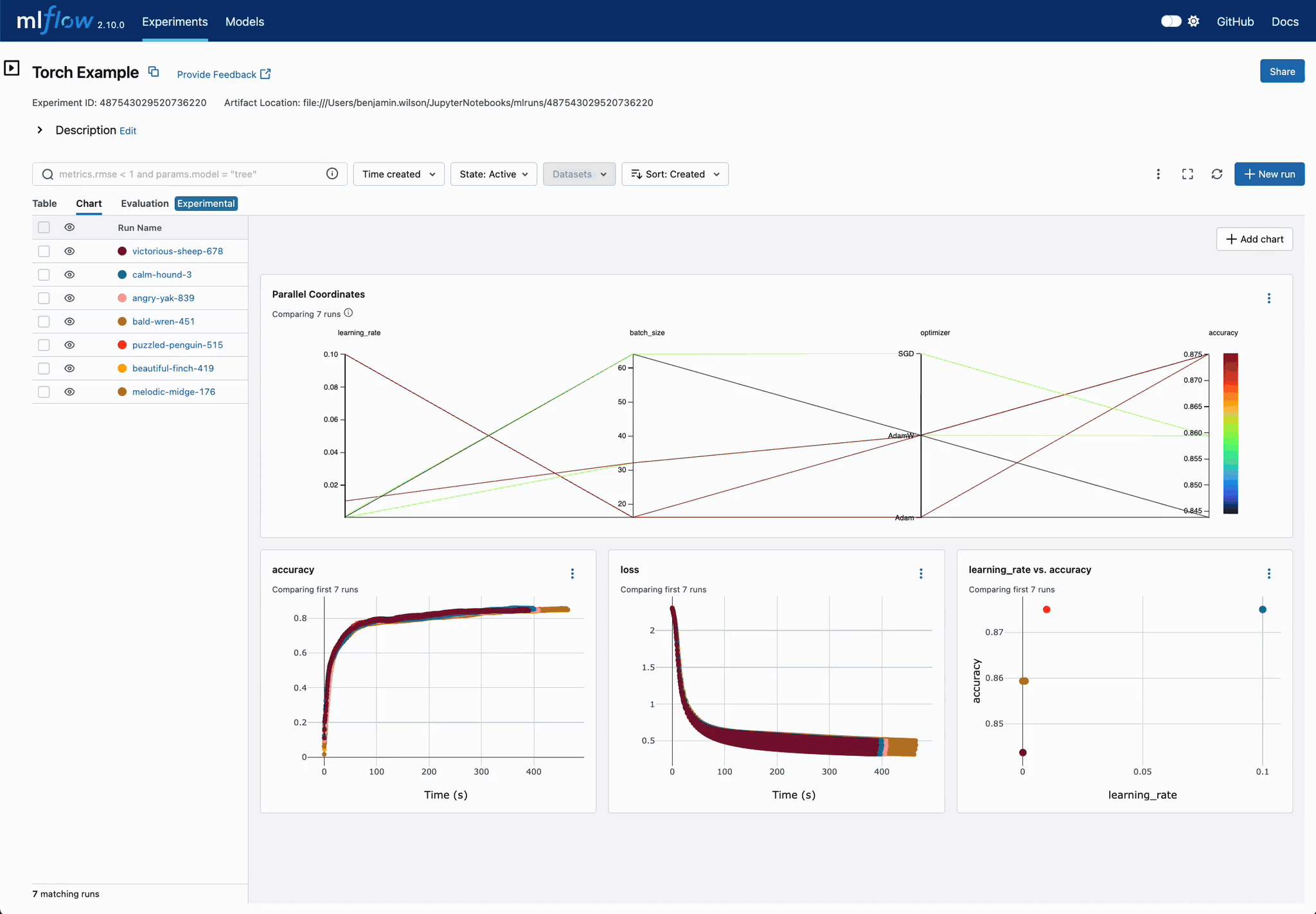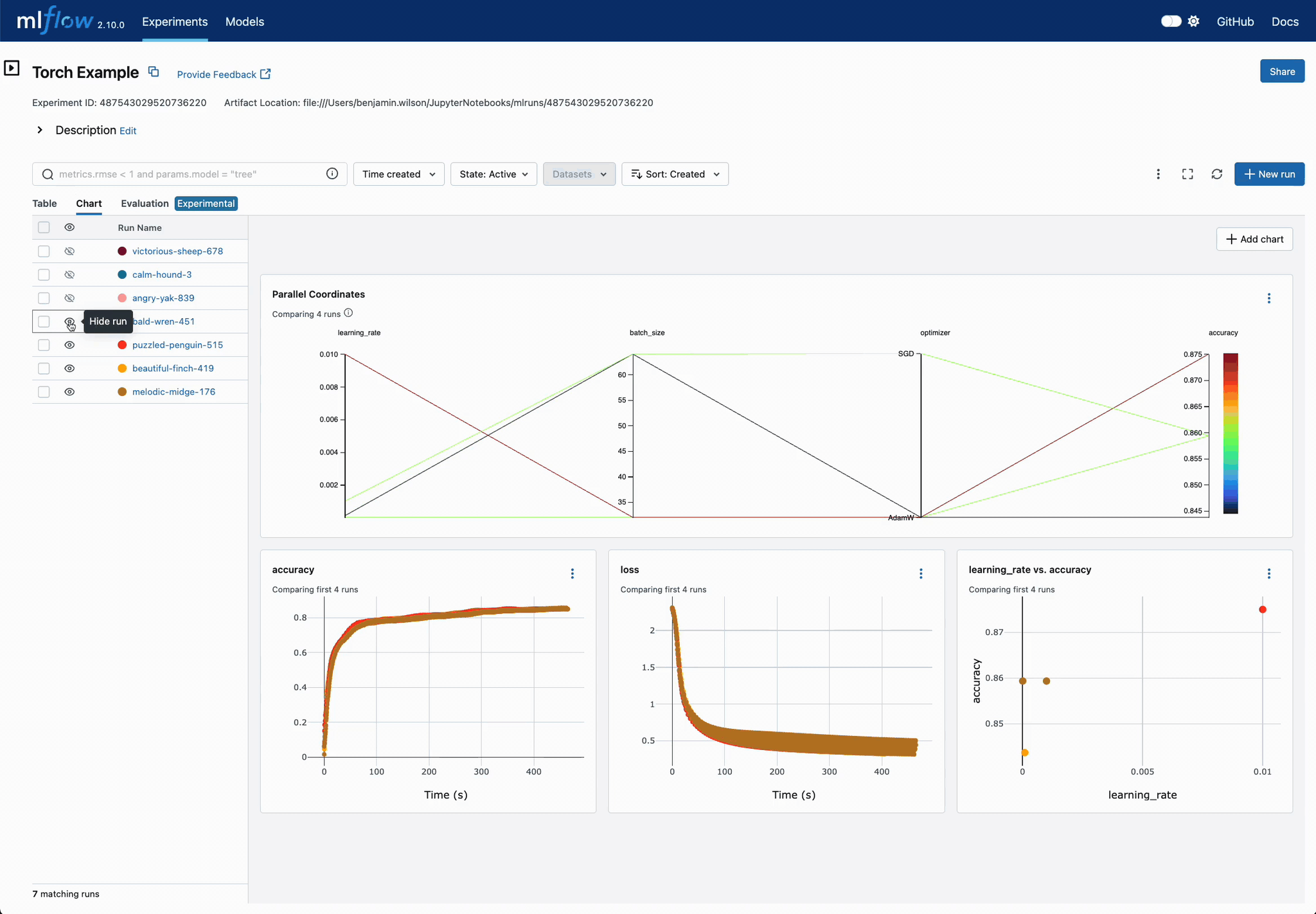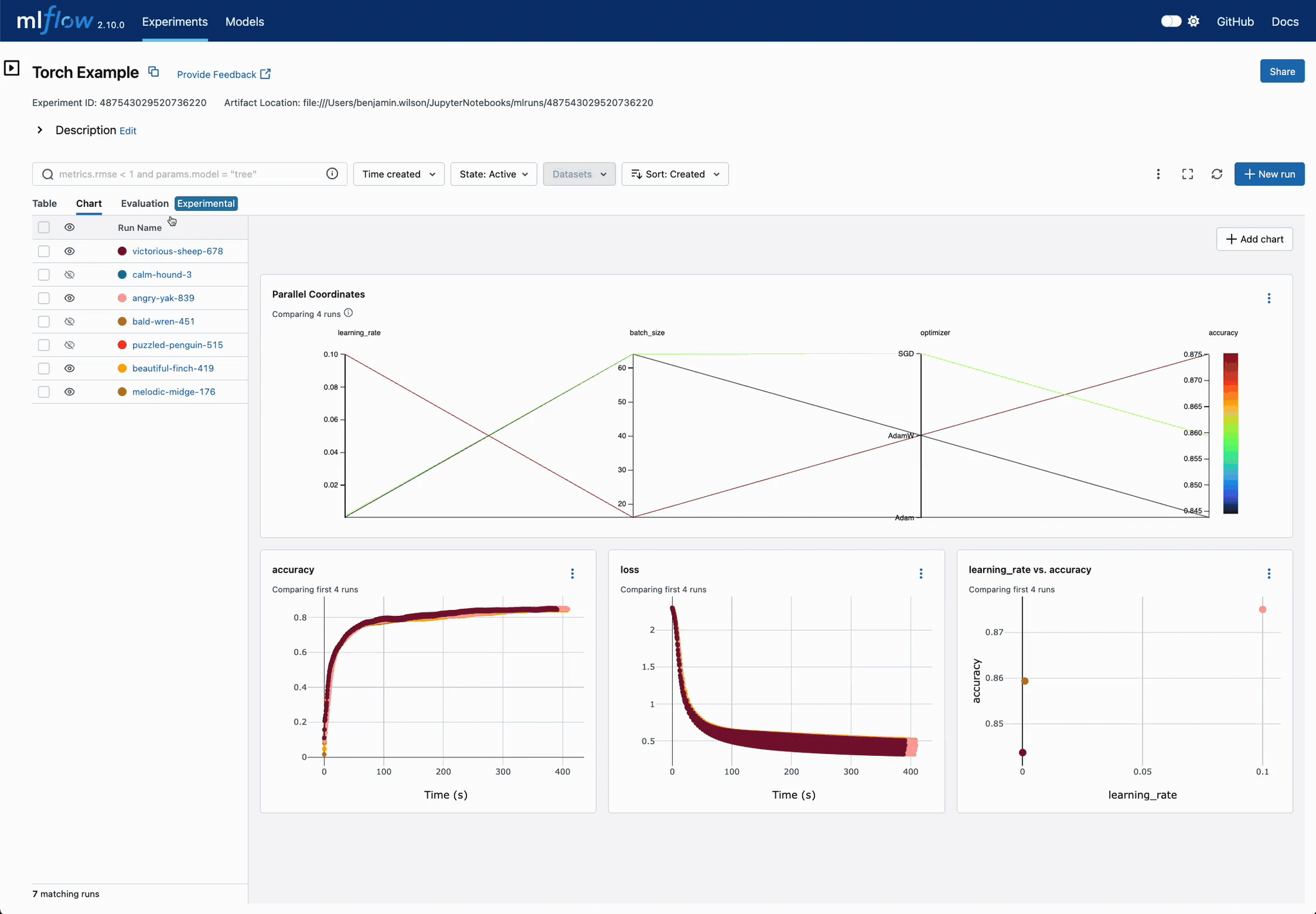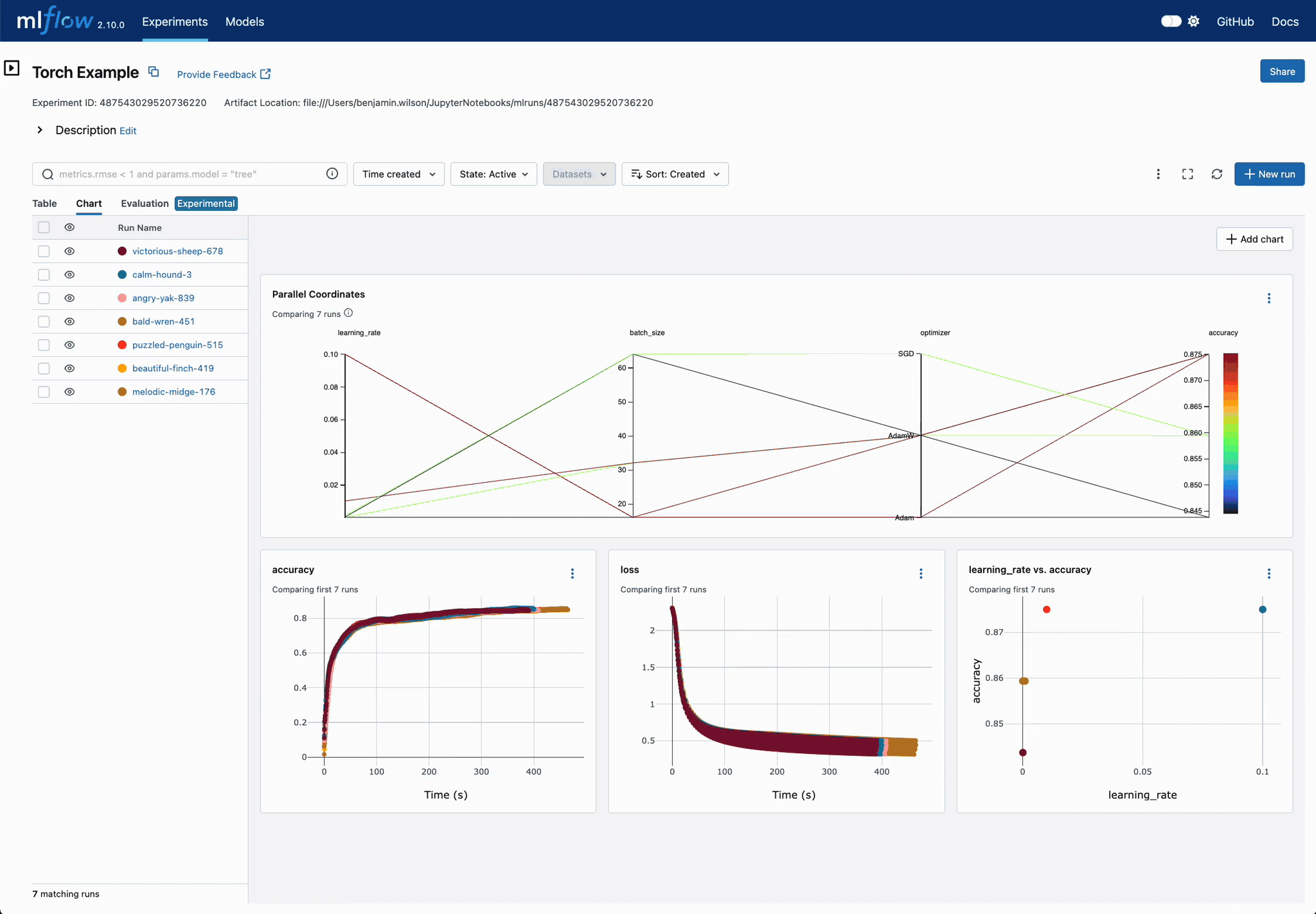
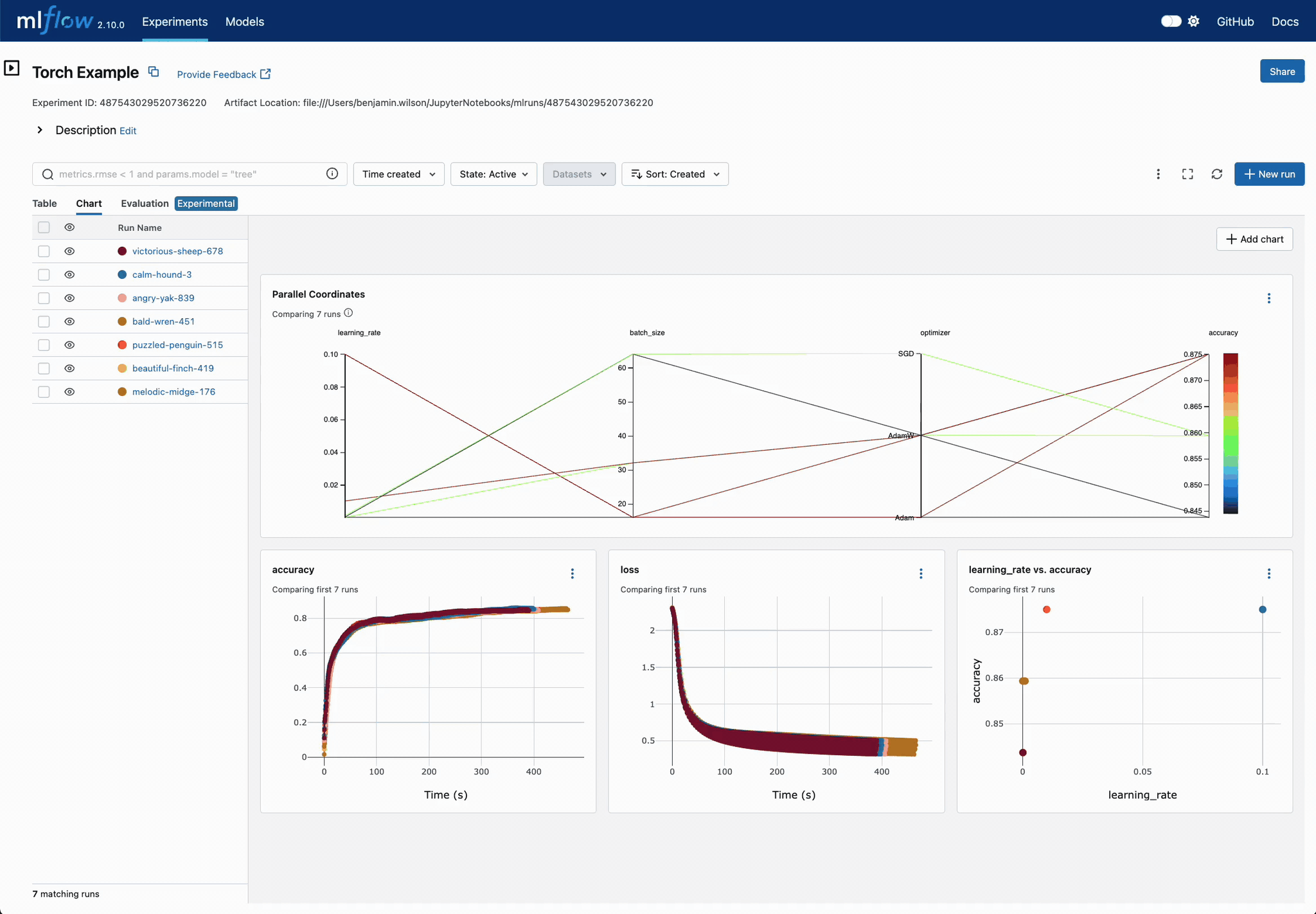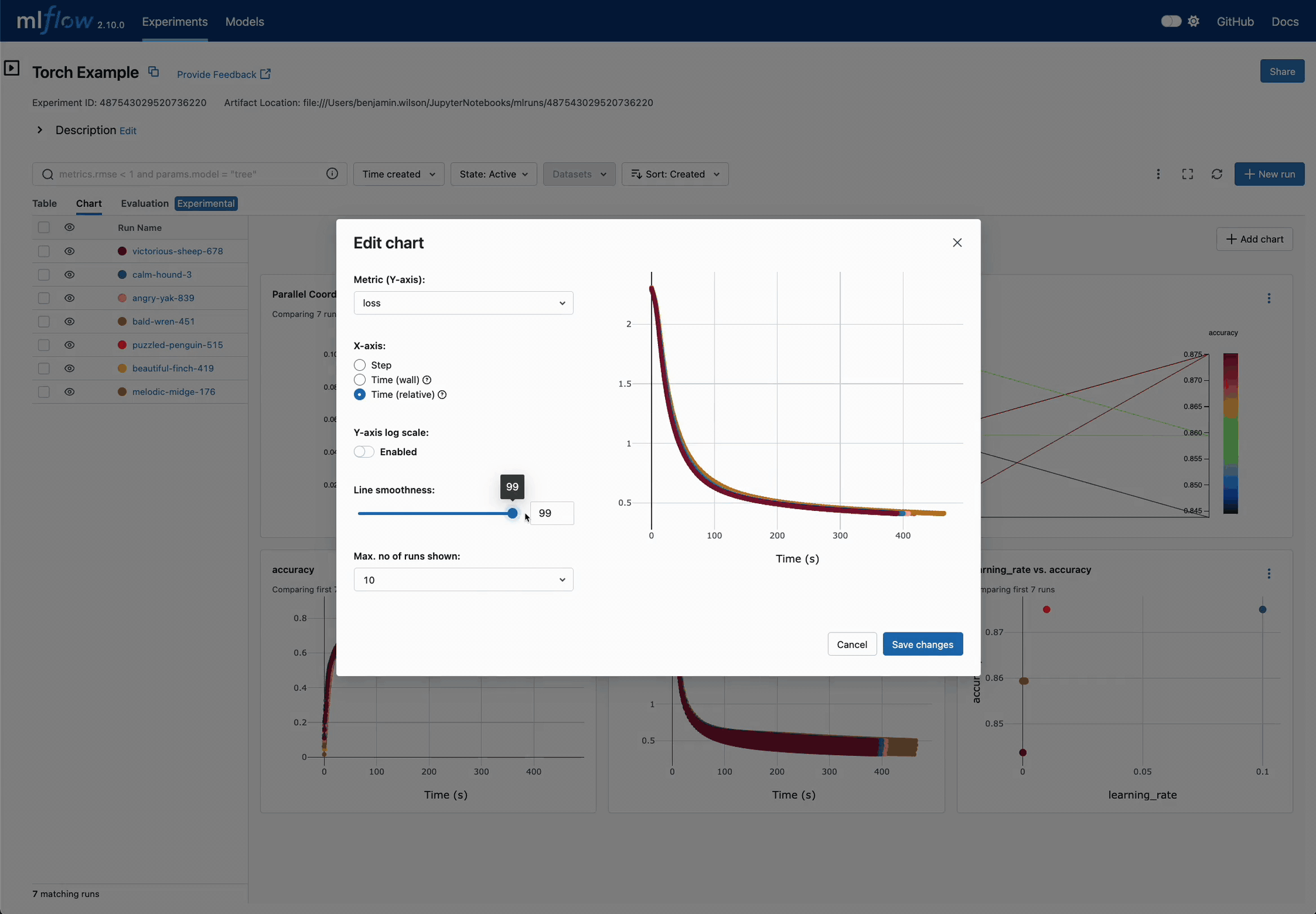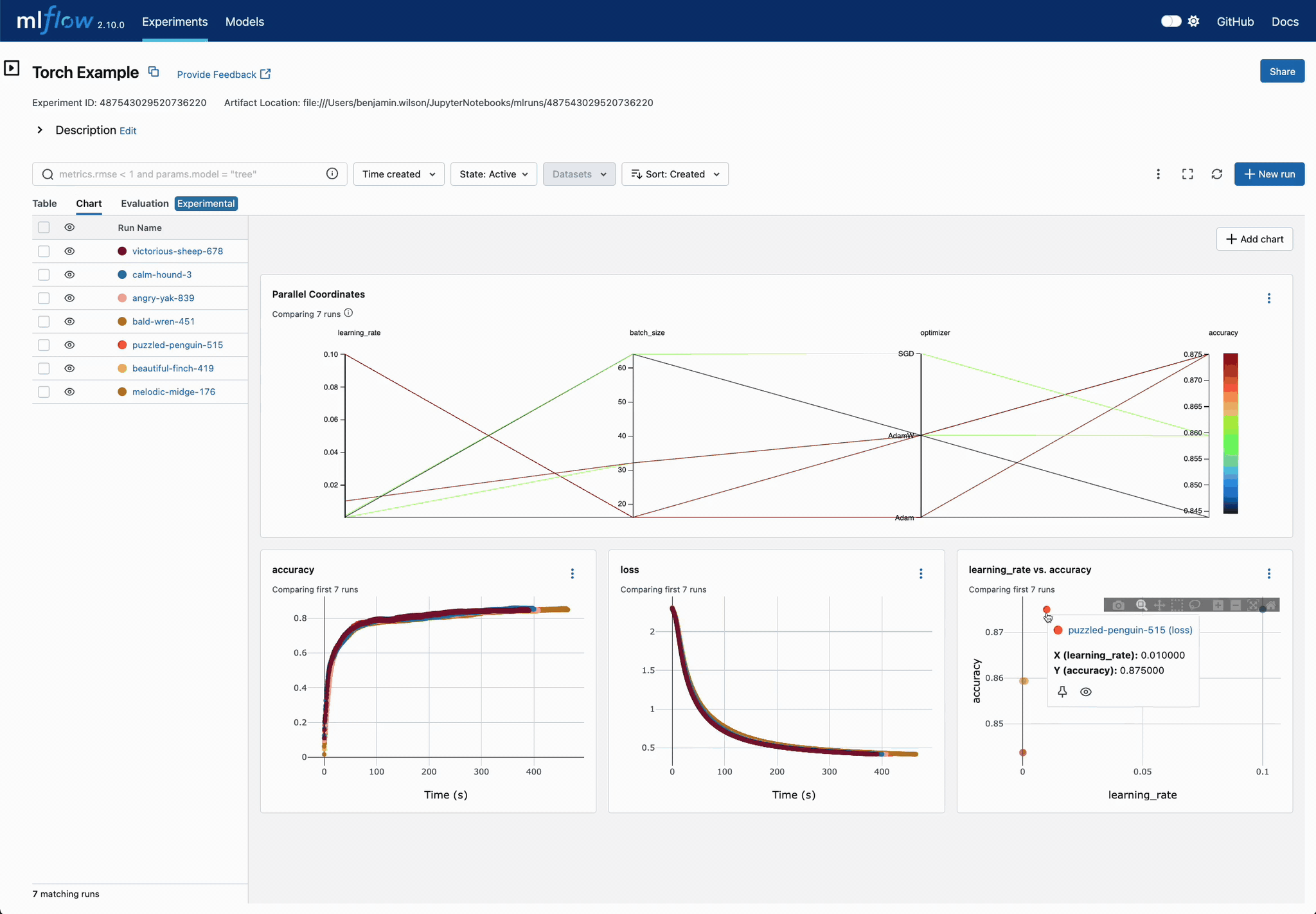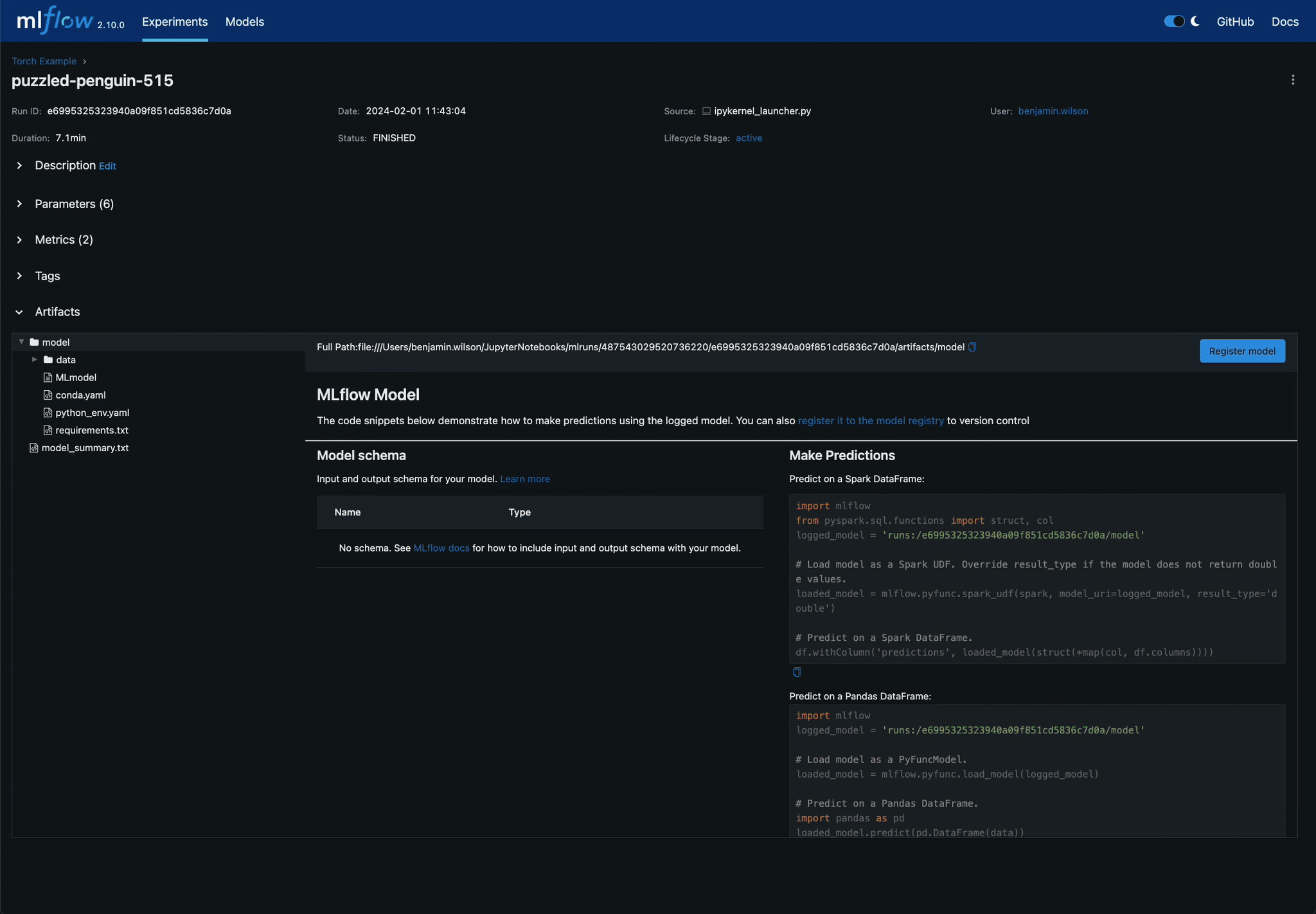
Chart Customization for DL Models
Easily customize charts for DL training run comparisons. Adjust visualizations to pinpoint optimal parameter settings, displaying optimization metrics across iterations in a unified view.
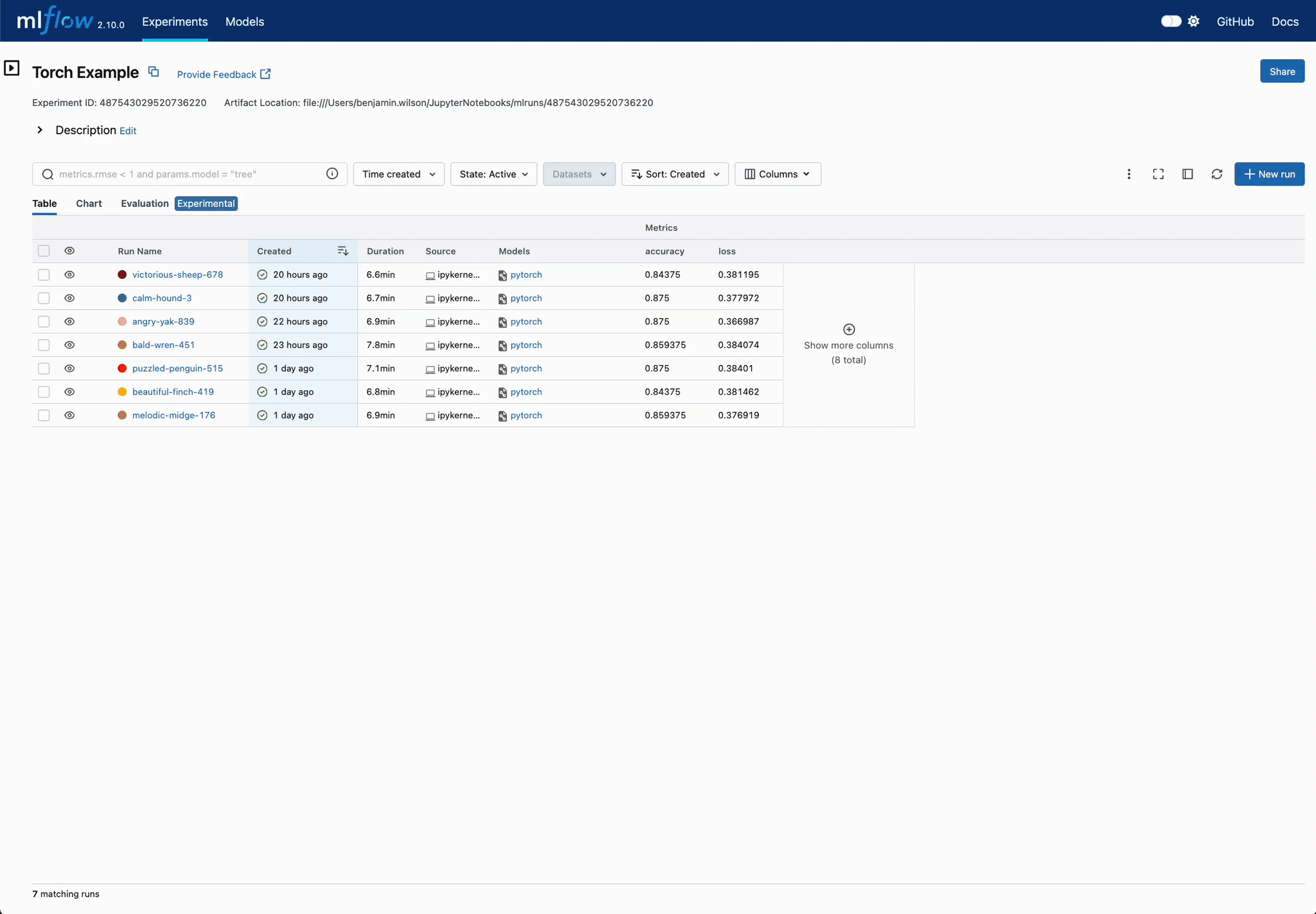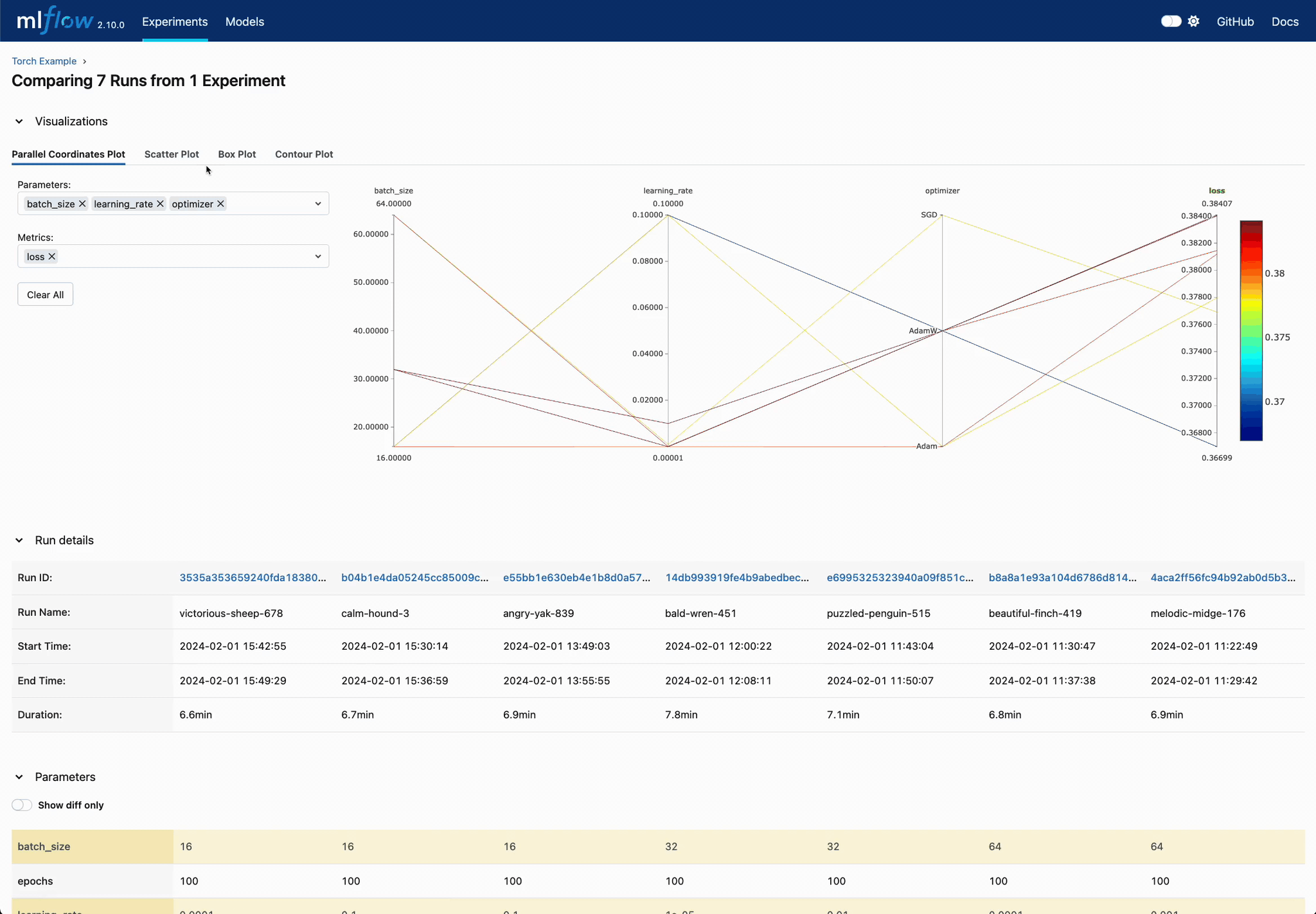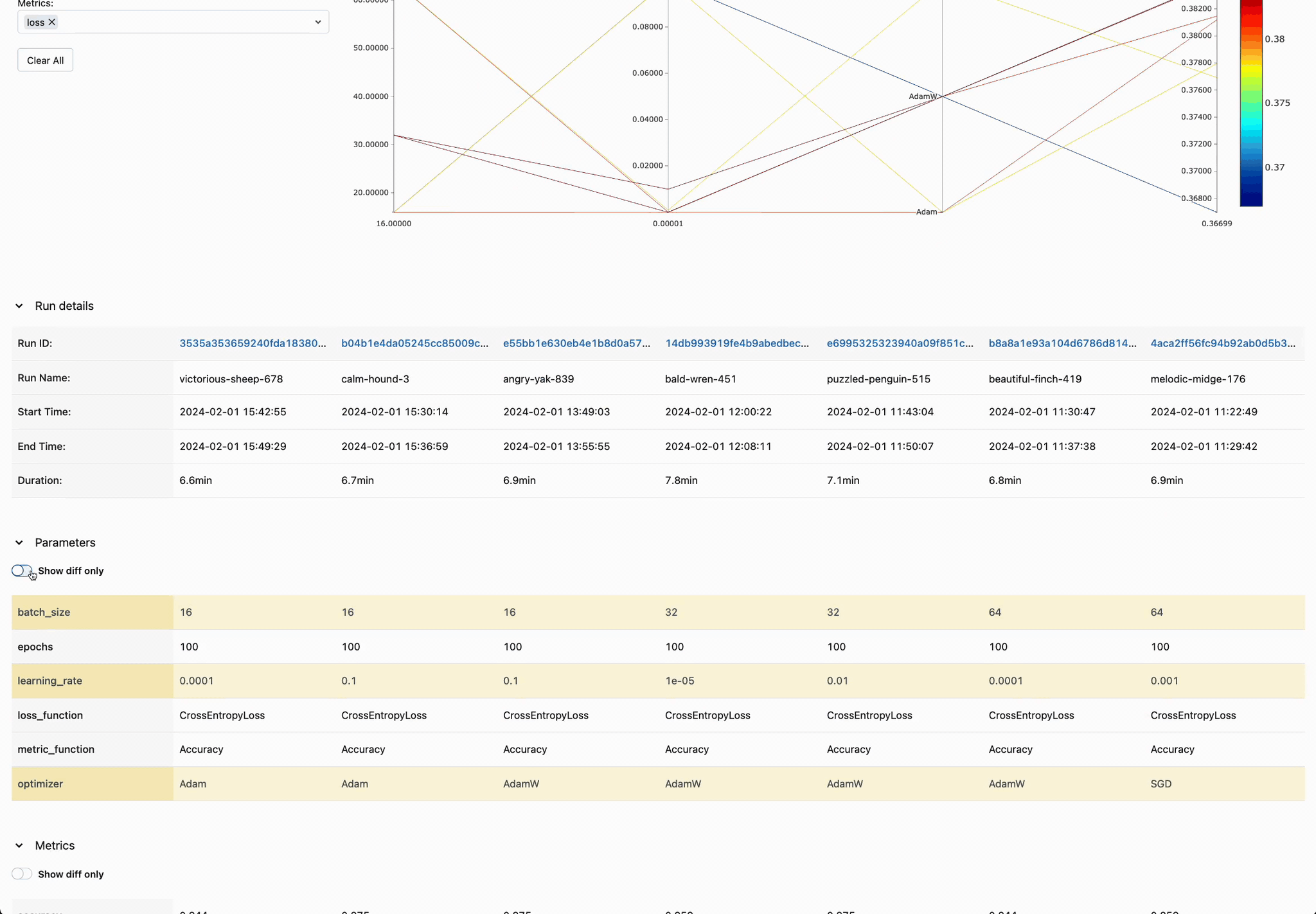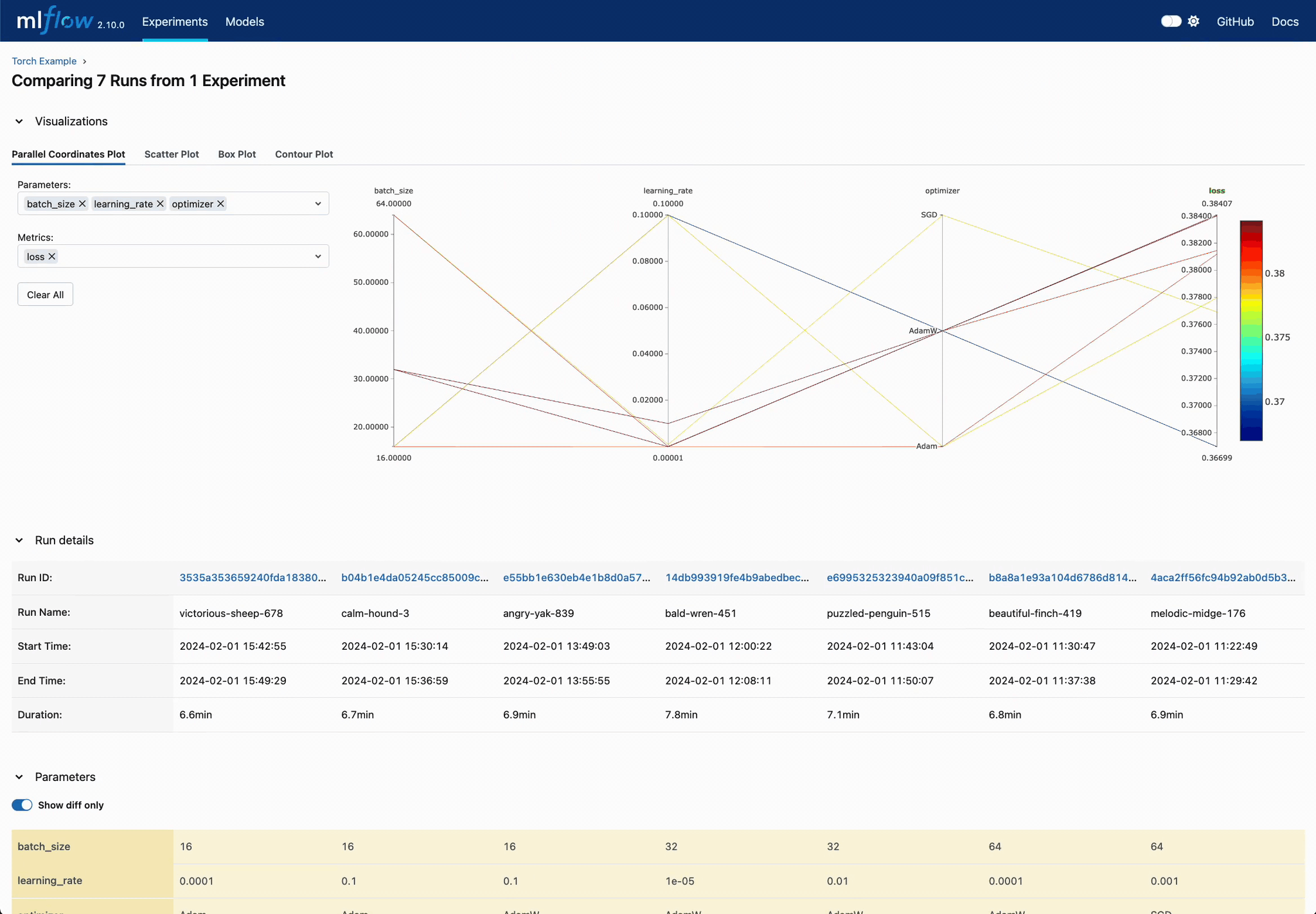
Enhanced Parameter and Metric Comparison
Analyze parameter relationships from a unified interface to refine tuning parameters, optimizing your DL models efficiently.
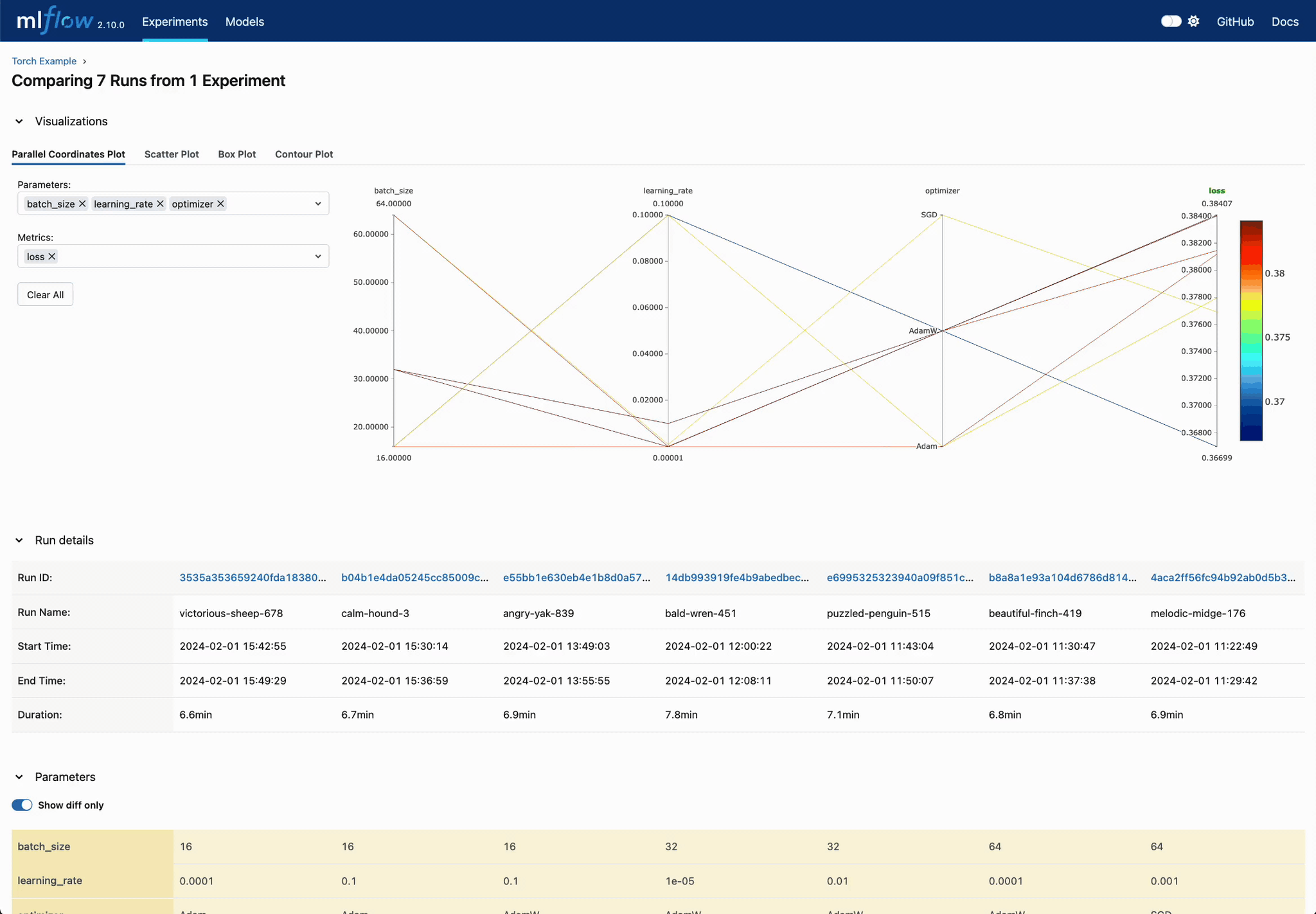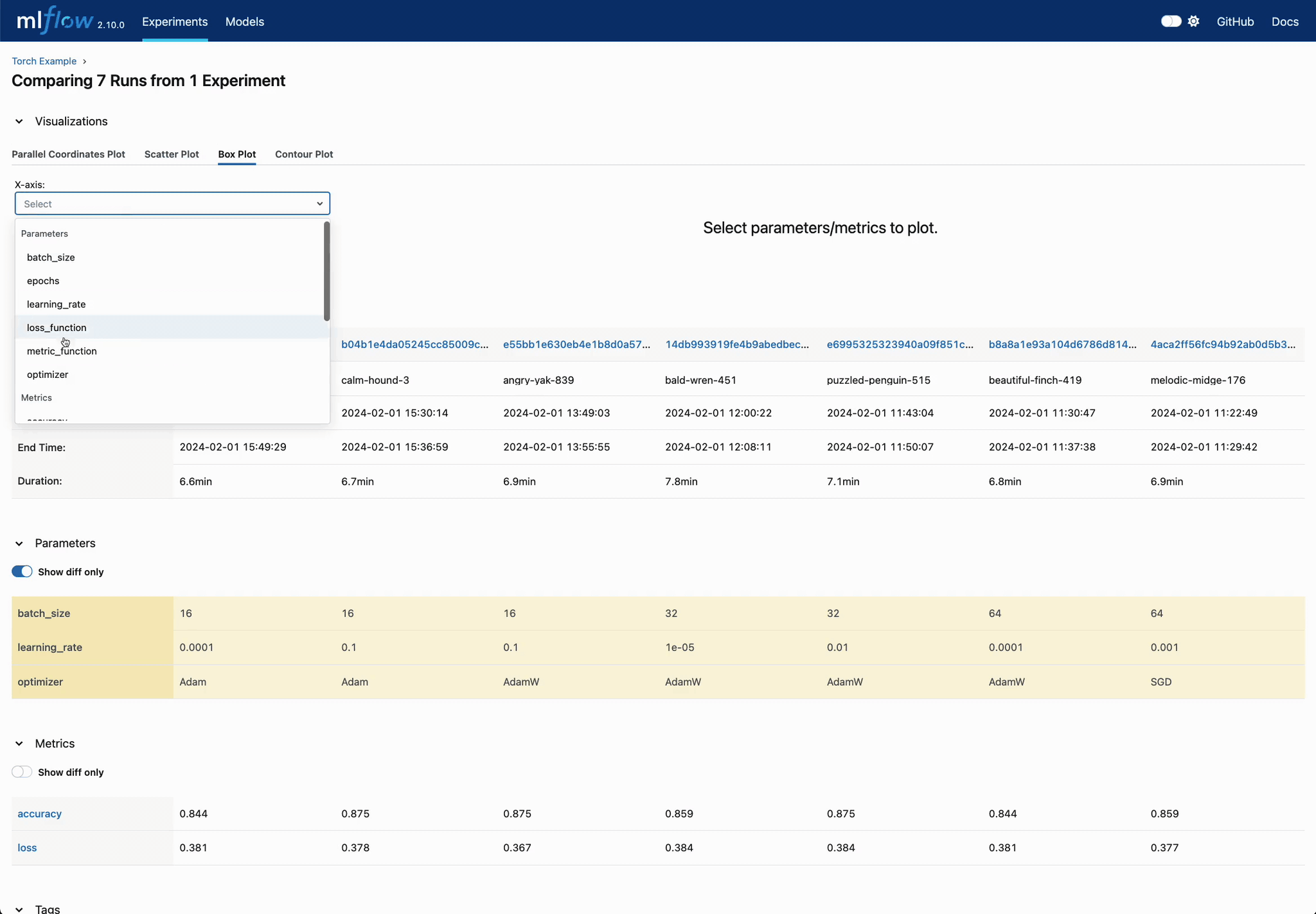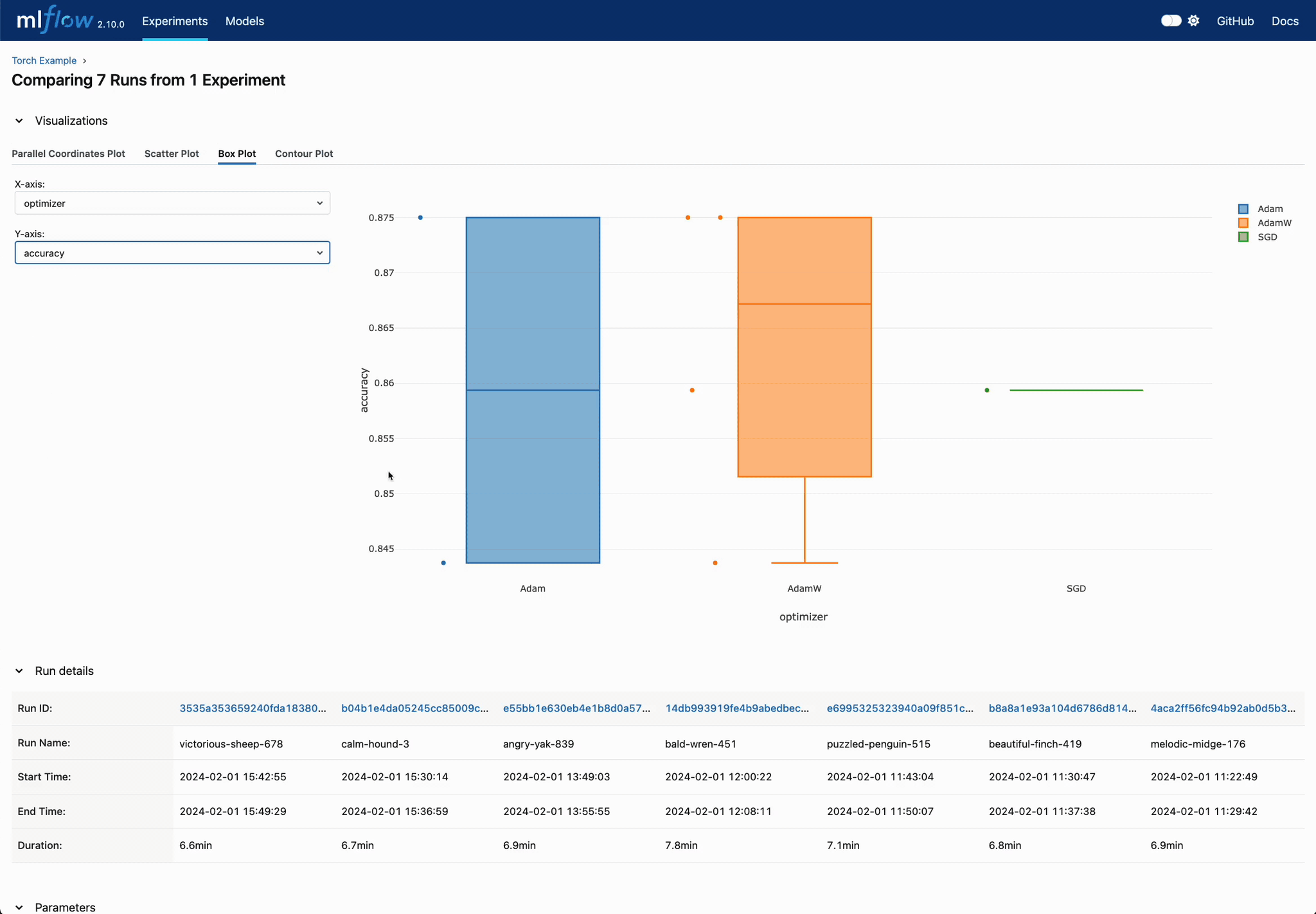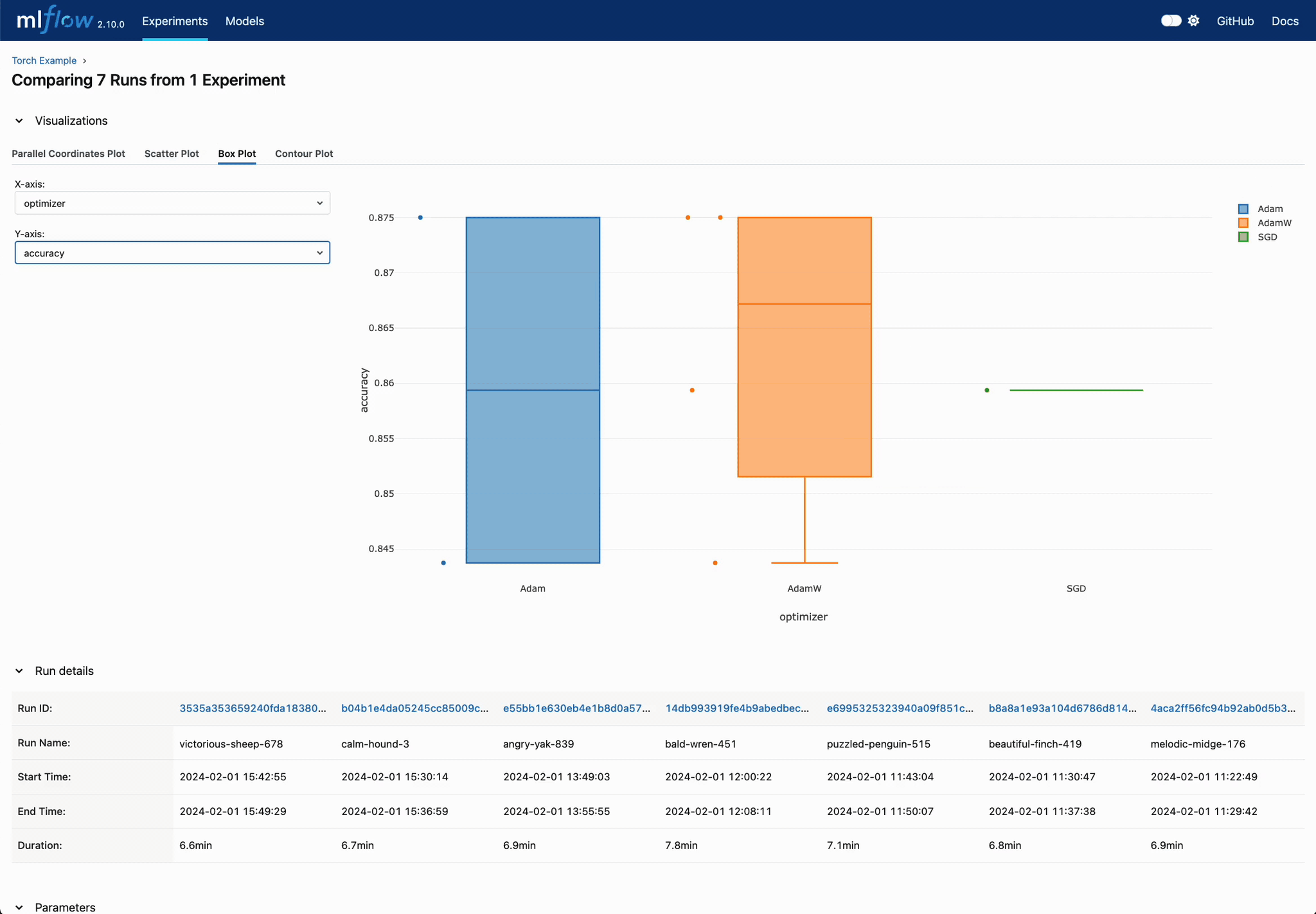
Statistical Evaluation of Categorical Parameters
Leverage boxplot visualizations for categorical parameter evaluation. Quickly discern the most effective settings for hyperparameter tuning.
Real-Time Training Tracking
Automatically monitor DL training progress over epochs with the MLflow UI. Instantly track results to validate your hypotheses, eliminating constant manual updates.
Model Registry
A centralized repository for your deep learning models:
Versioning: Handle multiple iterations and versions of deep learning models, facilitating comparison or reversion.
Annotations: Attach notes, training datasets, or other relevant metadata to models.
Lifecycle Stages: Clearly define the stage of each model version, ensuring clarity in deployment and further fine-tuning.
Model Deployment
Transition deep learning models from training to real-world applications:
Consistency: Ensure models, especially those with GPU dependencies, behave consistently across different deployment environments.
Docker and GPU Support: Deploy in containerized environments, ensuring all dependencies, including GPU support, are encapsulated.
Scalability: From deploying a single model to serving multiple distributed deep learning models, MLflow scales as per your requirements.
Native Library Support
MLflow has native integrations with common deep learning libraries, such as PyTorch, Keras and Tensorflow, so you can plug MLflow into your workflow easily to elevate your deep learning projects.
For detailed guide on how to integrate MLflow with these libraries, refer to the following pages: