mlflow.fastai
The mlflow.fastai module provides an API for logging and loading fast.ai models. This module
exports fast.ai models with the following flavors:
- fastai (native) format
This is the main flavor that can be loaded back into fastai.
mlflow.pyfuncProduced for use by generic pyfunc-based deployment tools and batch inference.
-
mlflow.fastai.autolog(log_models=True, log_datasets=True, disable=False, exclusive=False, disable_for_unsupported_versions=False, silent=False, registered_model_name=None, extra_tags=None)[source] Note
Autologging is known to be compatible with the following package versions:
2.4.1<=fastai<=2.7.18. Autologging may not succeed when used with package versions outside of this range.Enable automatic logging from Fastai to MLflow.
Logs loss and any other metrics specified in the fit function, and optimizer data as parameters. Model checkpoints are logged as artifacts to a ‘models’ directory.
MLflow will also log the parameters of the EarlyStoppingCallback and OneCycleScheduler callbacks
- Parameters
log_models – If
True, trained models are logged as MLflow model artifacts. IfFalse, trained models are not logged.log_datasets – If
True, dataset information is logged to MLflow Tracking. IfFalse, dataset information is not logged.disable – If
True, disables the Fastai autologging integration. IfFalse, enables the Fastai autologging integration.exclusive – If
True, autologged content is not logged to user-created fluent runs. IfFalse, autologged content is logged to the active fluent run, which may be user-created.disable_for_unsupported_versions – If
True, disable autologging for versions of fastai that have not been tested against this version of the MLflow client or are incompatible.silent – If
True, suppress all event logs and warnings from MLflow during Fastai autologging. IfFalse, show all events and warnings during Fastai autologging.registered_model_name – If given, each time a model is trained, it is registered as a new model version of the registered model with this name. The registered model is created if it does not already exist.
extra_tags – A dictionary of extra tags to set on each managed run created by autologging.
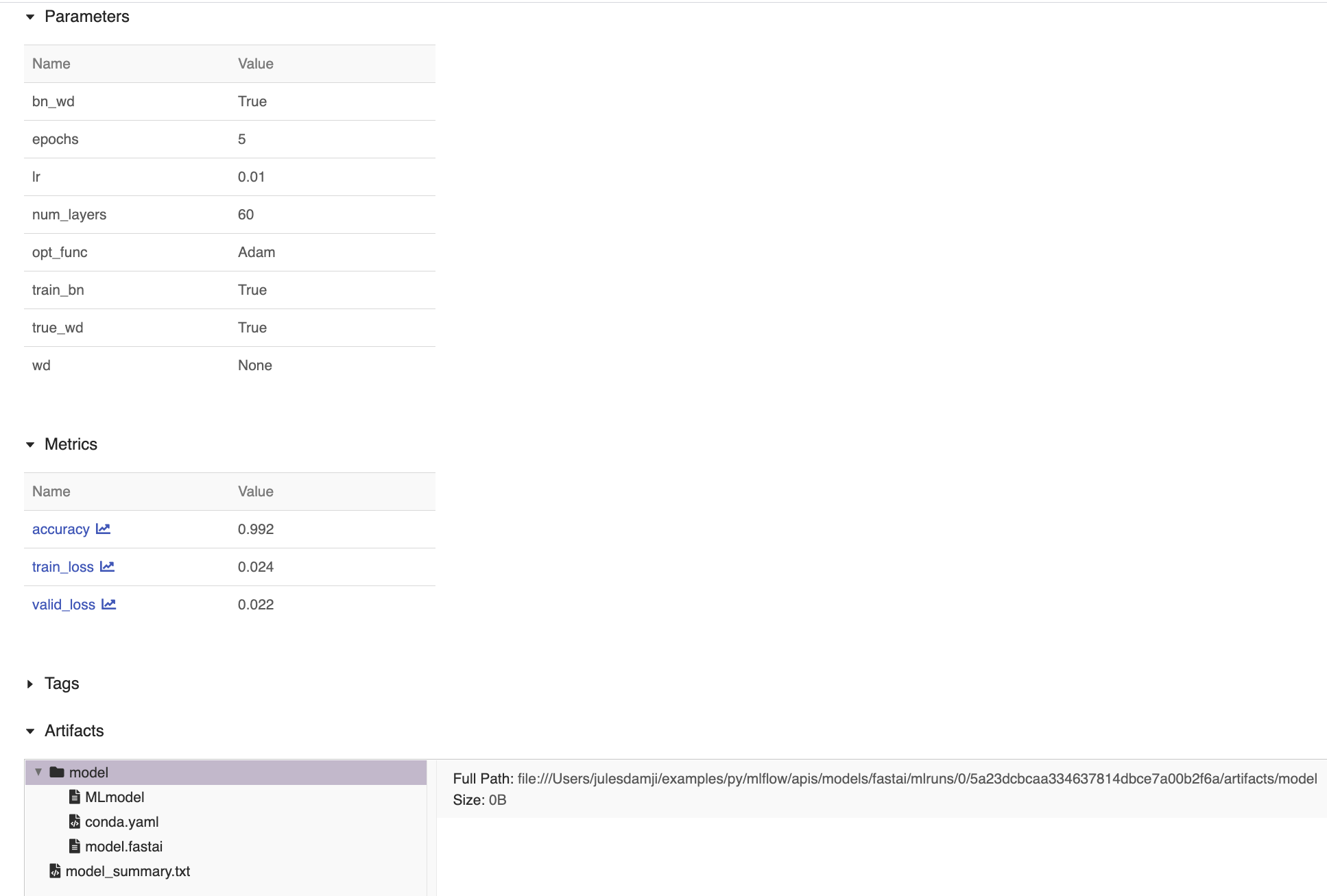
# This is a modified example from # https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow/tree/master/examples/fastai # demonstrating autolog capabilities. import fastai.vision as vis import mlflow.fastai from mlflow import MlflowClient def print_auto_logged_info(r): tags = {k: v for k, v in r.data.tags.items() if not k.startswith("mlflow.")} artifacts = [f.path for f in MlflowClient().list_artifacts(r.info.run_id, "model")] print(f"run_id: {r.info.run_id}") print(f"artifacts: {artifacts}") print(f"params: {r.data.params}") print(f"metrics: {r.data.metrics}") print(f"tags: {tags}") def main(epochs=5, learning_rate=0.01): # Download and untar the MNIST data set path = vis.untar_data(vis.URLs.MNIST_SAMPLE) # Prepare, transform, and normalize the data data = vis.ImageDataBunch.from_folder( path, ds_tfms=(vis.rand_pad(2, 28), []), bs=64 ) data.normalize(vis.imagenet_stats) # Create CNN the Learner model model = vis.cnn_learner(data, vis.models.resnet18, metrics=vis.accuracy) # Enable auto logging mlflow.fastai.autolog() # Start MLflow session with mlflow.start_run() as run: model.fit(epochs, learning_rate) # fetch the auto logged parameters, metrics, and artifacts print_auto_logged_info(mlflow.get_run(run_id=run.info.run_id)) main()
run_id: 5a23dcbcaa334637814dbce7a00b2f6a artifacts: ['model/MLmodel', 'model/conda.yaml', 'model/model.fastai'] params: {'wd': 'None', 'bn_wd': 'True', 'opt_func': 'Adam', 'epochs': '5', ' train_bn': 'True', 'num_layers': '60', 'lr': '0.01', 'true_wd': 'True'} metrics: {'train_loss': 0.024, 'accuracy': 0.99214, 'valid_loss': 0.021} # Tags model summary omitted too long tags: {...}
-
mlflow.fastai.get_default_conda_env(include_cloudpickle=False)[source] - Returns
The default Conda environment for MLflow Models produced by calls to
save_model()andlog_model().
-
mlflow.fastai.get_default_pip_requirements(include_cloudpickle=False)[source] - Returns
A list of default pip requirements for MLflow Models produced by this flavor. Calls to
save_model()andlog_model()produce a pip environment that, at minimum, contains these requirements.
-
mlflow.fastai.load_model(model_uri, dst_path=None)[source] Load a fastai model from a local file or a run.
- Parameters
model_uri –
The location, in URI format, of the MLflow model. For example:
/Users/me/path/to/local/modelrelative/path/to/local/models3://my_bucket/path/to/modelruns:/<mlflow_run_id>/run-relative/path/to/model
For more information about supported URI schemes, see Referencing Artifacts.
dst_path – The local filesystem path to which to download the model artifact. This directory must already exist. If unspecified, a local output path will be created.
- Returns
A fastai model (an instance of fastai.Learner).
import mlflow.fastai # Define the Learner model model = ... # log the fastai Leaner model with mlflow.start_run() as run: model.fit(epochs, learning_rate) mlflow.fastai.log_model(model, "model") # Load the model for scoring model_uri = f"runs:/{run.info.run_id}/model" loaded_model = mlflow.fastai.load_model(model_uri) results = loaded_model.predict(predict_data)
-
mlflow.fastai.log_model(fastai_learner, artifact_path, conda_env=None, code_paths=None, registered_model_name=None, signature: mlflow.models.signature.ModelSignature = None, input_example: Union[pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, numpy.ndarray, dict, list, csr_matrix, csc_matrix, str, bytes, tuple] = None, await_registration_for=300, pip_requirements=None, extra_pip_requirements=None, metadata=None, **kwargs)[source] Log a fastai model as an MLflow artifact for the current run.
- Parameters
fastai_learner – Fastai model (an instance of fastai.Learner) to be saved.
artifact_path – Run-relative artifact path.
conda_env –
Either a dictionary representation of a Conda environment or the path to a conda environment yaml file. If provided, this describes the environment this model should be run in. At a minimum, it should specify the dependencies contained in
get_default_conda_env(). IfNone, a conda environment with pip requirements inferred bymlflow.models.infer_pip_requirements()is added to the model. If the requirement inference fails, it falls back to usingget_default_pip_requirements(). pip requirements fromconda_envare written to a piprequirements.txtfile and the full conda environment is written toconda.yaml. The following is an example dictionary representation of a conda environment:{ "name": "mlflow-env", "channels": ["conda-forge"], "dependencies": [ "python=3.8.15", { "pip": [ "fastai==x.y.z" ], }, ], }
code_paths – A list of local filesystem paths to Python file dependencies (or directories containing file dependencies). These files are prepended to the system path when the model is loaded.
registered_model_name – This argument may change or be removed in a future release without warning. If given, create a model version under
registered_model_name, also creating a registered model if one with the given name does not exist.signature –
Describes model input and output Schema. The model signature can be inferred from datasets with valid model input (e.g. the training dataset with target column omitted) and valid model output (e.g. model predictions generated on the training dataset), for example:
from mlflow.models import infer_signature train = df.drop_column("target_label") predictions = ... # compute model predictions signature = infer_signature(train, predictions)
input_example – one or several instances of valid model input. The input example is used as a hint of what data to feed the model. It will be converted to a Pandas DataFrame and then serialized to json using the Pandas split-oriented format, or a numpy array where the example will be serialized to json by converting it to a list. Bytes are base64-encoded. When the
signatureparameter isNone, the input example is used to infer a model signature.await_registration_for – Number of seconds to wait for the model version to finish being created and is in
READYstatus. By default, the function waits for five minutes. Specify 0 or None to skip waiting.pip_requirements – Either an iterable of pip requirement strings (e.g.
["fastai", "-r requirements.txt", "-c constraints.txt"]) or the string path to a pip requirements file on the local filesystem (e.g."requirements.txt"). If provided, this describes the environment this model should be run in. IfNone, a default list of requirements is inferred bymlflow.models.infer_pip_requirements()from the current software environment. If the requirement inference fails, it falls back to usingget_default_pip_requirements(). Both requirements and constraints are automatically parsed and written torequirements.txtandconstraints.txtfiles, respectively, and stored as part of the model. Requirements are also written to thepipsection of the model’s conda environment (conda.yaml) file.extra_pip_requirements –
Either an iterable of pip requirement strings (e.g.
["pandas", "-r requirements.txt", "-c constraints.txt"]) or the string path to a pip requirements file on the local filesystem (e.g."requirements.txt"). If provided, this describes additional pip requirements that are appended to a default set of pip requirements generated automatically based on the user’s current software environment. Both requirements and constraints are automatically parsed and written torequirements.txtandconstraints.txtfiles, respectively, and stored as part of the model. Requirements are also written to thepipsection of the model’s conda environment (conda.yaml) file.Warning
The following arguments can’t be specified at the same time:
conda_envpip_requirementsextra_pip_requirements
This example demonstrates how to specify pip requirements using
pip_requirementsandextra_pip_requirements.metadata – Custom metadata dictionary passed to the model and stored in the MLmodel file.
kwargs – kwargs to pass to fastai.Learner.export method.
- Returns
A ModelInfo instance that contains the metadata of the logged model.
import fastai.vision as vis import mlflow.fastai from mlflow import MlflowClient def main(epochs=5, learning_rate=0.01): # Download and untar the MNIST data set path = vis.untar_data(vis.URLs.MNIST_SAMPLE) # Prepare, transform, and normalize the data data = vis.ImageDataBunch.from_folder( path, ds_tfms=(vis.rand_pad(2, 28), []), bs=64 ) data.normalize(vis.imagenet_stats) # Create the CNN Learner model model = vis.cnn_learner(data, vis.models.resnet18, metrics=vis.accuracy) # Start MLflow session and log model with mlflow.start_run() as run: model.fit(epochs, learning_rate) mlflow.fastai.log_model(model, "model") # fetch the logged model artifacts artifacts = [ f.path for f in MlflowClient().list_artifacts(run.info.run_id, "model") ] print(f"artifacts: {artifacts}") main()
-
mlflow.fastai.save_model(fastai_learner, path, conda_env=None, code_paths=None, mlflow_model=None, signature: mlflow.models.signature.ModelSignature = None, input_example: Union[pandas.core.frame.DataFrame, numpy.ndarray, dict, list, csr_matrix, csc_matrix, str, bytes, tuple] = None, pip_requirements=None, extra_pip_requirements=None, metadata=None, **kwargs)[source] Save a fastai Learner to a path on the local file system.
- Parameters
fastai_learner – fastai Learner to be saved.
path – Local path where the model is to be saved.
conda_env –
Either a dictionary representation of a Conda environment or the path to a conda environment yaml file. If provided, this describes the environment this model should be run in. At a minimum, it should specify the dependencies contained in
get_default_conda_env(). IfNone, a conda environment with pip requirements inferred bymlflow.models.infer_pip_requirements()is added to the model. If the requirement inference fails, it falls back to usingget_default_pip_requirements(). pip requirements fromconda_envare written to a piprequirements.txtfile and the full conda environment is written toconda.yaml. The following is an example dictionary representation of a conda environment:{ "name": "mlflow-env", "channels": ["conda-forge"], "dependencies": [ "python=3.8.15", { "pip": [ "fastai==x.y.z" ], }, ], }
code_paths – A list of local filesystem paths to Python file dependencies (or directories containing file dependencies). These files are prepended to the system path when the model is loaded.
mlflow_model – MLflow model config this flavor is being added to.
signature –
Describes model input and output Schema. The model signature can be inferred from datasets with valid model input (e.g. the training dataset with target column omitted) and valid model output (e.g. model predictions generated on the training dataset), for example:
from mlflow.models import infer_signature train = df.drop_column("target_label") predictions = ... # compute model predictions signature = infer_signature(train, predictions)
input_example – one or several instances of valid model input. The input example is used as a hint of what data to feed the model. It will be converted to a Pandas DataFrame and then serialized to json using the Pandas split-oriented format, or a numpy array where the example will be serialized to json by converting it to a list. Bytes are base64-encoded. When the
signatureparameter isNone, the input example is used to infer a model signature.pip_requirements – Either an iterable of pip requirement strings (e.g.
["fastai", "-r requirements.txt", "-c constraints.txt"]) or the string path to a pip requirements file on the local filesystem (e.g."requirements.txt"). If provided, this describes the environment this model should be run in. IfNone, a default list of requirements is inferred bymlflow.models.infer_pip_requirements()from the current software environment. If the requirement inference fails, it falls back to usingget_default_pip_requirements(). Both requirements and constraints are automatically parsed and written torequirements.txtandconstraints.txtfiles, respectively, and stored as part of the model. Requirements are also written to thepipsection of the model’s conda environment (conda.yaml) file.extra_pip_requirements –
Either an iterable of pip requirement strings (e.g.
["pandas", "-r requirements.txt", "-c constraints.txt"]) or the string path to a pip requirements file on the local filesystem (e.g."requirements.txt"). If provided, this describes additional pip requirements that are appended to a default set of pip requirements generated automatically based on the user’s current software environment. Both requirements and constraints are automatically parsed and written torequirements.txtandconstraints.txtfiles, respectively, and stored as part of the model. Requirements are also written to thepipsection of the model’s conda environment (conda.yaml) file.Warning
The following arguments can’t be specified at the same time:
conda_envpip_requirementsextra_pip_requirements
This example demonstrates how to specify pip requirements using
pip_requirementsandextra_pip_requirements.metadata – Custom metadata dictionary passed to the model and stored in the MLmodel file.
kwargs – kwargs to pass to
Learner.savemethod.
import os import mlflow.fastai # Create a fastai Learner model model = ... # Start MLflow session and save model to current working directory with mlflow.start_run(): model.fit(epochs, learning_rate) mlflow.fastai.save_model(model, "model") # Load saved model for inference model_uri = "{}/{}".format(os.getcwd(), "model") loaded_model = mlflow.fastai.load_model(model_uri) results = loaded_model.predict(predict_data)